B–4
B
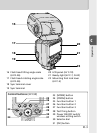
About the SB-900
Main functions
Flash modes and functions on the SB-900
i-TTL mode
(kD-2)
The camera controls the SB SB-900’s flash output level by measuring the light
reflected from the subject when the SB-900 fires a series of monitor pre-flashes.
Auto-Aperture flash mode
(kD-5)
The SB-900 controls the flash output level by measuring the flash illumination reflected
back from the subject using the sensor for Non-TTL auto flash and combining this with
information from the camera, such as the ISO sensitivity and the aperture setting.
Non-TTL Auto flash mode
(kD-8)
The SB-900 controls the flash output level by measuring the flash illumination
reflected back from the subject using the sensor for Non-TTL auto flash.
Distance Priority manual flash mode
(kD-11)
If you preset the aperture and the distance to the subject, the SB SB-900 will
automatically take control of correct light output.
Manual flash mode
(kD-14)
By setting the aperture and the flash output level, you can manually set the
exposure and the distance to the subject.
Repeating flash mode
(kD-17)
The SB-900 fires repeatedly to create stroboscopic multiple-exposure effects. This
operation is useful when shooting fast-moving subjects.
Switching illumination pattern
(kD-24)
You can select one of three types of illumination pattern (standard, center-weighted
and even) in accordance with your objective.
Bounce flash
(kD-26)
By tilting or rotating the flash head, you can bounce the light off a ceiling or wall to
make use of reflected light.
Close-up flash photography
(kD-30)
Close up flash photography can be achieved with use of the built-in wide-flash
adapter and the flash head tilted down.
Using color filters
(kD-33)
You can compensate for the color of a light source or create interesting effects by
changing the light from the filters to a different color.
Flash output level compensation/Exposure compensation
(kD-37)
Flash output level compensation is performed by modifying the flash output level for
the flash illuminated subject only. Exposure compensation is performed by intentionally
modifying the correct exposure to modify both the subject and background exposure.