506501-01 Page 7 of 48Issue 1031
air is brought into the house for combustion, negative
pressure (outside pressure is greater than inside pressure)
will build to the point that a down draft can occur in the furnace
vent pipe or chimney. As a result, combustion gases enter
the living space creating a potentially dangerous situation.
In the absence of local codes concerning air for combustion
and ventilation, use the guidelines and procedures in this
section to install these furnaces to ensure efficient and safe
operation. You must consider combustion air needs and
requirements for exhaust vents and gas piping. A portion of
this information has been reprinted with permission from
the National Fuel Gas Code (ANSI-Z223.1/NFPA 54). This
reprinted material is not the complete and official position of
ANSI on the referenced subject, which is represented only
by the standard in its entirely.
In Canada, refer to the CSA B149 Installation codes.
All gas-fired appliances require air for the combustion
process. If sufficient combustion air is not available, the
furnace or other appliance will operate inefficiently and
unsafely. Enough air must be provided to meet the needs
of all fuel-burning appliances and appliances such as exhaust
fans which force air out of the house. When fireplaces,
exhaust fans, or clothes dryers are used at the same time
as the furnace, much more air is required to ensure proper
combustion and to prevent a down draft. Insufficient air
causes incomplete combustion which can result in carbon
monoxide.
In addition to providing combustion air, fresh outdoor air
dilutes contaminants in the indoor air. These contaminants
may include bleaches, adhesives, detergents, solvents and
other contaminants which can corrode furnace components.
The requirements for providing air for combustion and
ventilation depend largely on whether the furnace is installed
in an unconfined or a confined space.
Unconfined Space
An unconfined space is an area such as a basement or
large equipment room with a volume greater than 50 cubic
feet (1.42 m³) per 1,000 Btu (.29 kW) per hour of the
combined input rating of all appliances installed in that space.
This space also includes adjacent rooms which are not
separated by a door. Though an area may appear to be
unconfined, it might be necessary to bring in outdoor air for
combustion if the structure does not provide enough air by
Do not install the furnace in a corrosive or contaminated
atmosphere. Meet all combustion and ventilation air
requirements, as well as all local codes.
CAUTION
infiltration. If the furnace is located in a building of tight
construction with weather stripping and caulking around the
windows and doors, follow the procedures in the “Air from
Outside” section.
Confined Space
A confined space is an area with a volume less than 50
cubic feet (1.42 m³) per 1,000 Btu (.29 kW) per hour of the
combined input rating of all appliances installed in that space.
This definition includes furnace closets or small equipment
rooms.
When the furnace is installed so that supply ducts carry air
circulated by the furnace to areas outside the space
containing the furnace, the return air must be handled by
ducts which are sealed to the furnace casing and which
terminate outside the space containing the furnace. This is
especially important when the furnace is mounted on a
platform in a confined space such as a closet or small
equipment room. Even a small leak around the base of the
unit at the platform or at the return air duct connection can
cause a potentially dangerous negative pressure condition.
Air for combustion and ventilation can be brought into the
confined space either from inside the building or from outside.
Air from Inside
If the confined space that houses the furnace adjoins a space
categorized as unconfined, air can be brought in by providing
two permanent openings between the two spaces. Each
opening must have a minimum free area of 1 square inch
(645 mm²) per 1,000 Btu (.29 kW) per hour of total input
rating of all gas-fired equipment in the confined space. Each
opening must be at least 100 square inches (64516 mm²).
One opening shall be within 12 inches (305 mm) of the top
of the enclosure and one opening within 12 inches (305 mm)
of the bottom. See Figure 4.
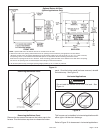
Figure 4
Equipment in Confined Space - All Air From Inside
NOTE: Each opening shall have a free area of at least one square
inch per 1,000 Btu (645 mm² per .29 kW) per hour of the total input
rating of all equipment in the enclosure, but not less than 100 square
inches (64546 mm²).