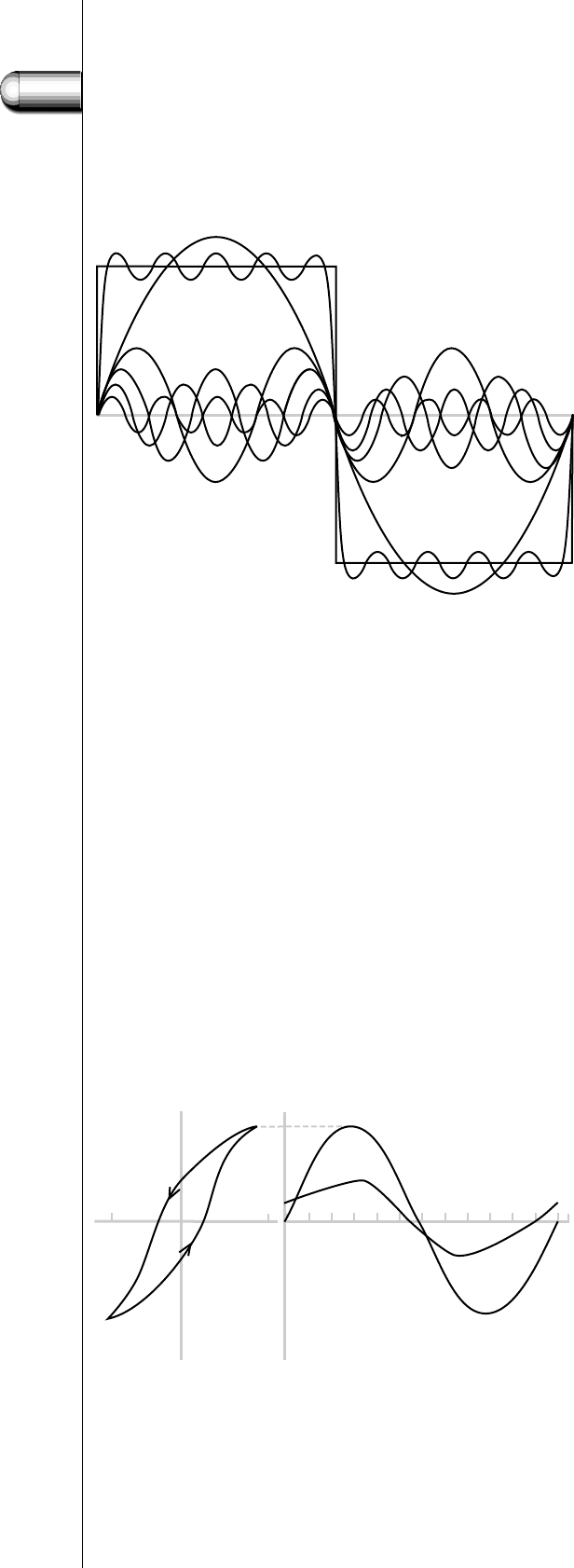
The second reason for the presence of harmonics in the lamp current
is the hysteresis of the ballast coil.With the aid of the relationship
between ballast voltage and ballast current (B-H curve of the ballast
coil, see Fig. 124), the resulting current can be found for any ballast
voltage. Even with a pure sine-wave ballast voltage there will be some
harmonics in the ballast current, but this effect is small, compared with
the harmonics caused by the lamp.
The impedance of the coil becomes higher for higher frequencies, so
in practice only odd harmonics up to the seventh are of any importance
for the lamp current.
Practical values in percentage of the fundamental for most inductively
stabilised discharge lamps are:
fundamental: 100 %
third harmonic: 10 %
fifth harmonic: 3 %
seventh harmonic: 2 %
ninth and higher harmonics: 1 % or lower
When the supply voltage contains harmonics, these values can change
somewhat, but the ballast coil prevents dramatic increases.
5
129
Fig. 123. Lamp voltage wave form constructed by the
odd harmonics from one to nine, according to
the formula:
f(t) = 4U/π(sin
ω
t + 1/3sin3
ω
t + 1/5sin5
ω
t + ....).
Fig. 124. Hysteresis curve of a typical
copper-iron ballast.
3.9 Harmonic distortion
1
3
5
7
9
0
π
2π
U
H,i
H,i
t
B,Φ,V
B,Φ,V


















