Parallel connection of two lamps on a common ballast is impossible
because of the negative characteristic of the fluorescent lamp.All the
current would flow through the lamp with the lower arc voltage.
Moreover, once the first lamp is ignited the lamp voltage is too low for
the ignitor of the second lamp to ignite this lamp.
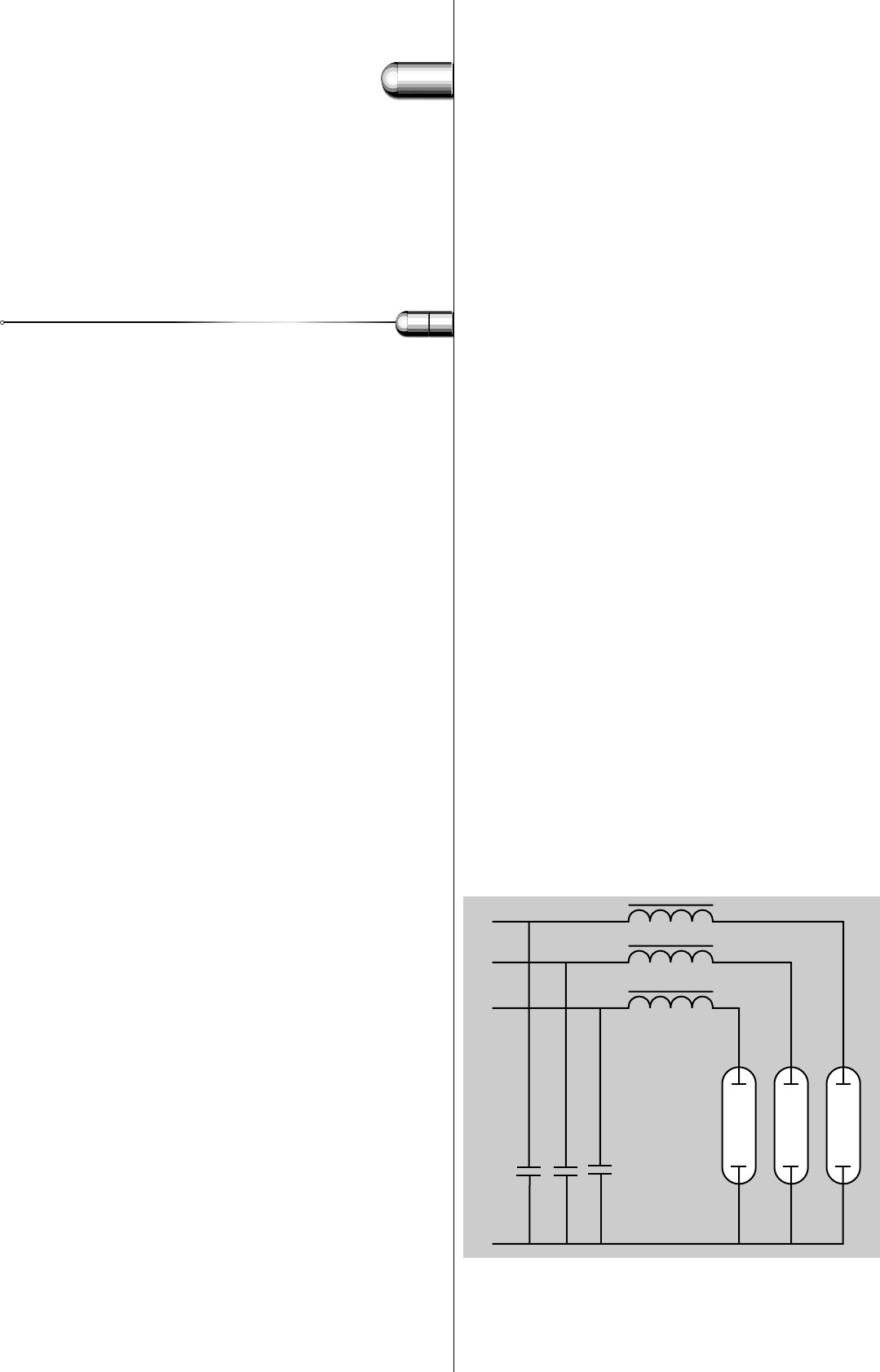
Neutral interruption and resonance
Normally each lamp circuit has its own compensating capacitor. In this
way every luminaire can be switched separately without influencing the
power factor.For the same reason lamp circuits based on phase-neutral
(230 V), are compensated with capacitors connected between each of
the phases and neutral.
In the phase-neutral network failure of one phase has no other effect
than to switch off the circuits on that phase. But if the neutral is not
connected, resonance will occur. For example, the current from phase
L1 via ballast and lamp 3 (see Fig. 118) can pass via capacitor C1 to
phase L3. So lamp 3 is energised by 400 V and stabilised by a ballast
with a capacitor in series.This will surely destroy components.
A good neutral is essential.
Moreover, when the neutral is interrupted and the loads on the phases
are not completely balanced ( i.e. the same wattage), then the voltage
across the smallest load will increase and much more power will be
consumed by that load.This will surely damage lamps and/or ballasts
(see Fig. 119).
Suppose there are five loads of 1000 Ω, one connected between L1
and neutral and four connected between L2 and neutral.The current
from L1 will be 230/1000 = 0.23 A and the power in the load will be
230 . 0.23 = 53 W.
The current from L2 will be four times higher (0.92 A) and the power
too: 212 W.
If the neutral is interrupted, the phase-phase voltage of 400 V will result
in a current which can be calculated from the resistances: 1000 Ω in
series with 4 times 1000 Ω parallel.
36
5
124
Fig. 118. Compensation in a
phase/neutral network.
3.5 Series connection of lamps
La
LaLa
B
B
B
N
1
2
3
C3
C2
C1
L
1
L
2
L
3


















