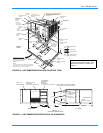
035-17233-000-C-0702
24 Unitary Products
ADJUSTMENT OF TEMPERATURE RISE
The temperature rise (or temperature difference between the
return air and the heated air from the furnace) must lie within
the range shown on the ETL rating plate and the data in Table
2.
After the temperature rise has been determined, the cfm can
be calculated as follows:
After about 20 minutes of operation, determine the furnace
temperature rise. Take readings of both the return air and the
heated air in the ducts (about six feet from the furnace) where
they will not be affected by radiant heat. Increase the blower
cfm to decrease the temperature rise; decrease the blower
cfm to increase the rise. Refer to Table 11 for blower motor
and drive data.
BELT DRIVE BLOWER
All units have belt drive single-speed blower motors. The vari-
able pitch pulley on the blower motor can be adjusted to
obtain the desired supply air CFM. Tighten belts enough to
prevent slipping. but do not over tighten. Belt deflection
should be between 1/4" and 1/2" per foot. Refer to Table 15
for blower motor and drive data.
CHECKING GAS INPUT
NATURAL GAS
1. Turn off all other gas appliances connected to the gas
meter.
2. With the furnace turned on, measure the time needed for
one revolution of the hand on the smallest dial on the
meter. A typical gas meter usually has a 1/2 or a 1 cubic
foot test dial.
3. Using the number of seconds for each revolution and the
size of the test dial increment, find the cubic feet of gas
consumed per hour from Table 18.
If the actual input is not within 5% of the furnace rating (with
allowance being made for the permissible range of the regu-
lator setting), replace the orifice spuds with spuds of the
proper size.
NOTE:
To find the Btu input, multiply the number of cubic feet
of gas consumed per hour by the Btu content of the gas in
your particular locality (contact your gas company for this
information - it varies widely from city to city.)
SECURE OWNER’S APPROVAL
When system is functioning properly, secure the owner’s
approval. Show him the location of all disconnect switches
and the thermostat. Teach him how to start and stop the unit
and how to adjust temperature settings within the limitations
of the system.
FIGURE 20 : PRESSURE DROP ACROSS A DRY
INDOOR COIL VS. SUPPLY AIR CFM
CFM
BtuhbInput 0.8×
1.08 °FbTempbRise×
--------------------------------------------------------
=
TABLE 18: GAS RATE - CUBIC FEET PER HOUR
1
1
Example: By actual measurement, it takes 13 seconds
for the hand on the 1-cubic foot dial to make a revolu-
tion with just a 300,000 Btuh furnace running. Read
across to the column in the table above, headed “1
Cubic Foot”, where you will see that 278 cubic feet of
gas per hour are consumed by the furnace at that rate.
Multiply 278 X 1050 (the Btu rating of the gas obtained
from the local gas company). The result is 292,425
Btuh, which is close to the 3000,000 Btuh rating of the
furnace.
SECONDS FOR 1 REV.
SIZE OF TEST DIAL
1/2 Cu. Ft. 1 Cu. Ft.
4 450 900
6 300 600
8 228 450
10 180 360
12 150 300
14 129 257
16 113 225
18 100 200
20 90 180
22 82 164
24 75 150
26 69 138
28 64 129