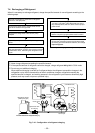
– 37 –
Nitrogen gas
cylinder
Pipe
Flow meter
M
Stop valve
From Nitrogen cylinder
Nitrogen
gas
Rubber plug
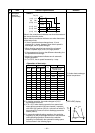
Piping
material
Copper - Copper
Copper - Iron
Iron - Iron
Used brazing
filler
Phosphor copper
Silver
Silver
Used
flux
Do not use
Paste flux
Vapor flux
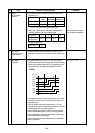
(2) Characteristics required for flux
• Activated temperature of flux coincides with
the brazing temperature.
• Due to a wide effective temperature range, flux
is hard to carbonize.
• It is easy to remove slag after brazing.
• The corrosive action to the treated metal and
brazing filler is minimum.
• It excels in coating performance and is harm-
less to the human body.
As the flux works in a complicated manner as
described above, it is necessary to select an
adequate type of flux according to the type and
shape of treated metal, type of brazing filler and
brazing method, etc.
(3) Types of flux
• Noncorrosive flux
Generally, it is a compound of borax and boric
acid.
It is effective in case where the brazing tem-
perature is higher than 800°C.
• Activated flux
Most of fluxes generally used for silver brazing
are this type.
It features an increased oxide film removing
capability due to the addition of compounds
such as potassium fluoride, potassium chloride
and sodium fluoride to the borax-boric acid
compound.
(4) Piping materials for brazing and used braz-
ing filler/flux
Do not enter flux into the refrigeration cycle.
When chlorine contained in the flux remains
within the pipe, the lubricating oil deteriorates.
Therefore, use a flux which does not contain
chlorine.
When adding water to the flux, use water
which does not contain chlorine (e.g. distilled
water or ion-exchange water).
Remove the flux after brazing.
7-5-3. Brazing
As brazing work requires sophisticated techniques,
experiences based upon a theoretical knowledge, it
must be performed by a person qualified.
In order to prevent the oxide film from occurring in
the pipe interior during brazing, it is effective to
proceed with brazing while letting dry Nitrogen gas
(N2) flow.
Never use gas other than Nitrogen gas.
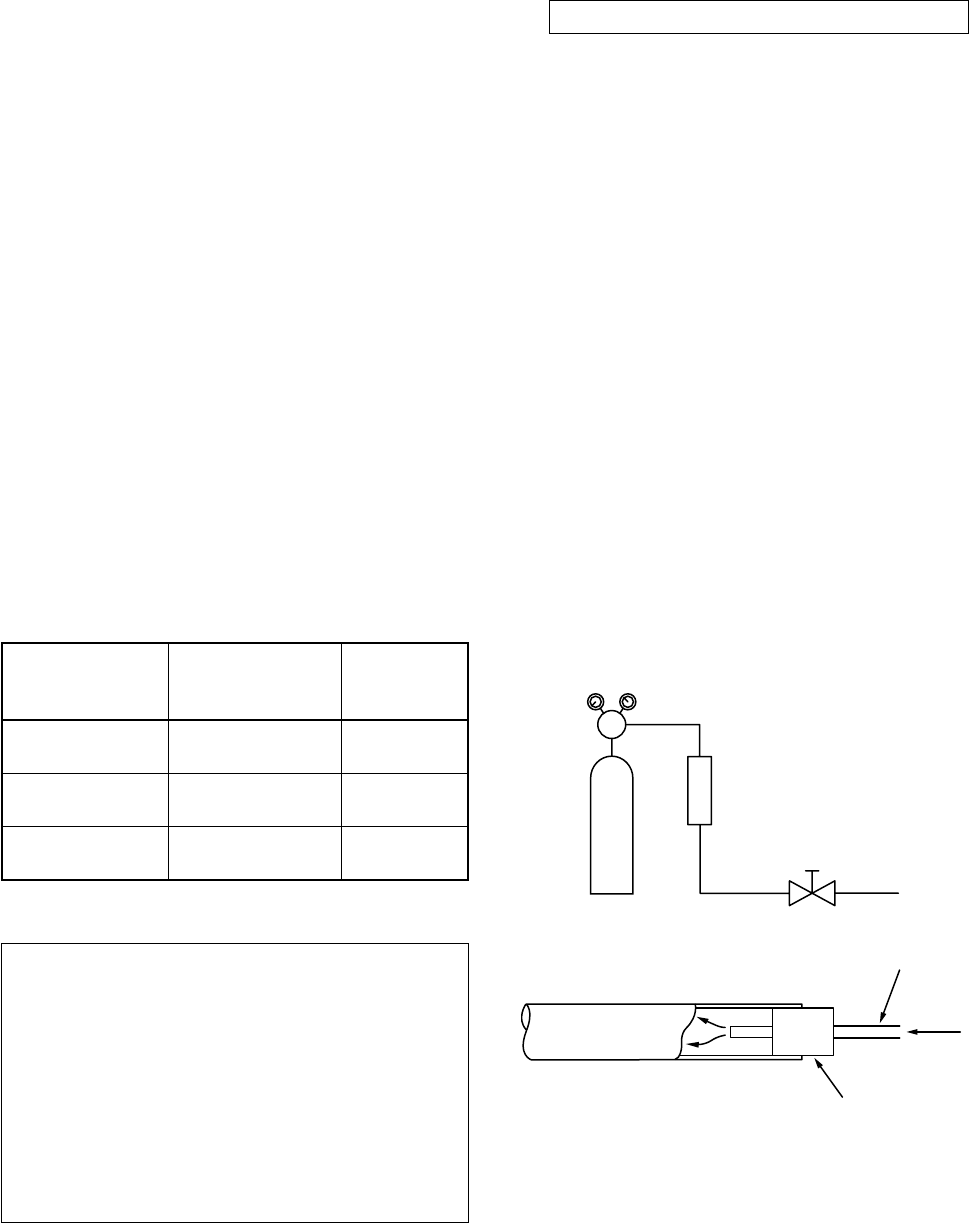
(1) Brazing method to prevent oxidation
Attach a reducing valve and a flow-meter to
the Nitrogen gas cylinder.
Use a copper pipe to direct the piping mate-
rial, and attach a flow-meter to the cylinder.
Apply a seal onto the clearance between the
piping material and inserted copper pipe for
Nitrogen in order to prevent backflow of the
Nitrogen gas.
When the Nitrogen gas is flowing, be sure to
keep the piping end open.
Adjust the flow rate of Nitrogen gas so that it
is lower than 0.05 m³/Hr or 0.02 MPa (0.2kgf/
cm²) by means of the reducing valve.
After performing the steps above, keep the
Nitrogen gas flowing until the pipe cools
down to a certain extent (temperature at
which pipes are touchable with hands).
Remove the flux completely after brazing.
Fig. 7-5-1 Prevention of oxidation during brazing