16
GAS-FIRED BOILER Boiler Manual
PART 5: BOILER PIPING
(CONTINUED)
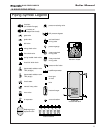
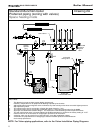
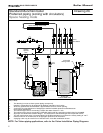
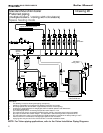
I. FILL AND PURGE HEATING SYSTEM
• Attach the hose to balance and purge hose
connector or drain valve and run hose to
nearest drain
• Close the other side of the balance and purge
valve or the shut off valve after the drain.
• Open first zone balance and purge or drain
valve to let water flow out the hose. If zone
valves are used, open the valves one at a
time manually. (Note: You should check valve
manufacturer’s instruction prior to opening
valves manually, so as not to damage the
valve.)
• Manually operate fill valve regulator. When
water runs out of the hose, while it’s
connected to the balance and purge valve or
drain you will see a steady stream of water
(without bubbles). Close balance and purge
valve or drain to stop the water from flowing.
Disconnect the hose and connect it to next
zone to be purged.
• Repeat this procedure for additional zones
(one at time).
Upon completion, make sure that the fill valve is
in automatic position and each zone balance and
purge or shut off is in an open position and zone
valves are positioned for automatic operation.
1. Glycol in hydronic applications which is
specially formulated for this purpose includes
inhibitors that prevent the glycol from
attacking metallic system components. Make
certain that the system fluid is checked for
the correct glycol concentration and inhibitor
level.
2. The glycol solution should be tested at least
once a year and as recommended by the
glycol manufacturer.
3. Anti-freeze solutions expand more than
water. For example a 50% by volume solution
expands 4.8% in volume for a temperature
increase from 32° F to 180° F, while water
expands 3% with the same temperature rise.
Allowances must be made for this expansion
in the system design.
4. A 30% mixture of glycol will result in a BTU
output loss of 15% with a 5% increase in
head against system circulator.
5. A 50% mixture of glycol will result in a BTU
output loss of 30% with a 50% increase in
head against system circulator.
CAUTION
For installation that incorporates standing Iron
Radiation and systems with manual vents at the
high points. Follow above section and starting
with the nearest manual air vent, open vent
until water flows out, then close vent. Repeat
procedure, working your way toward furthest
air vent. It may be necessary to install a basket
strainer in an older system where larger
amounts of sediment may be present. Annual
cleaning of the strainer may be necessary.
WARNING
Use only inhibited propylene glycol solutions
which are specially formulated for hydronic
systems. Ethylene glycol is toxic and can attack
gaskets and seals used in hydronic systems.
Glycol mixtures should not exceed 50%.
N/R = Not Recommended
N/A = Not Available
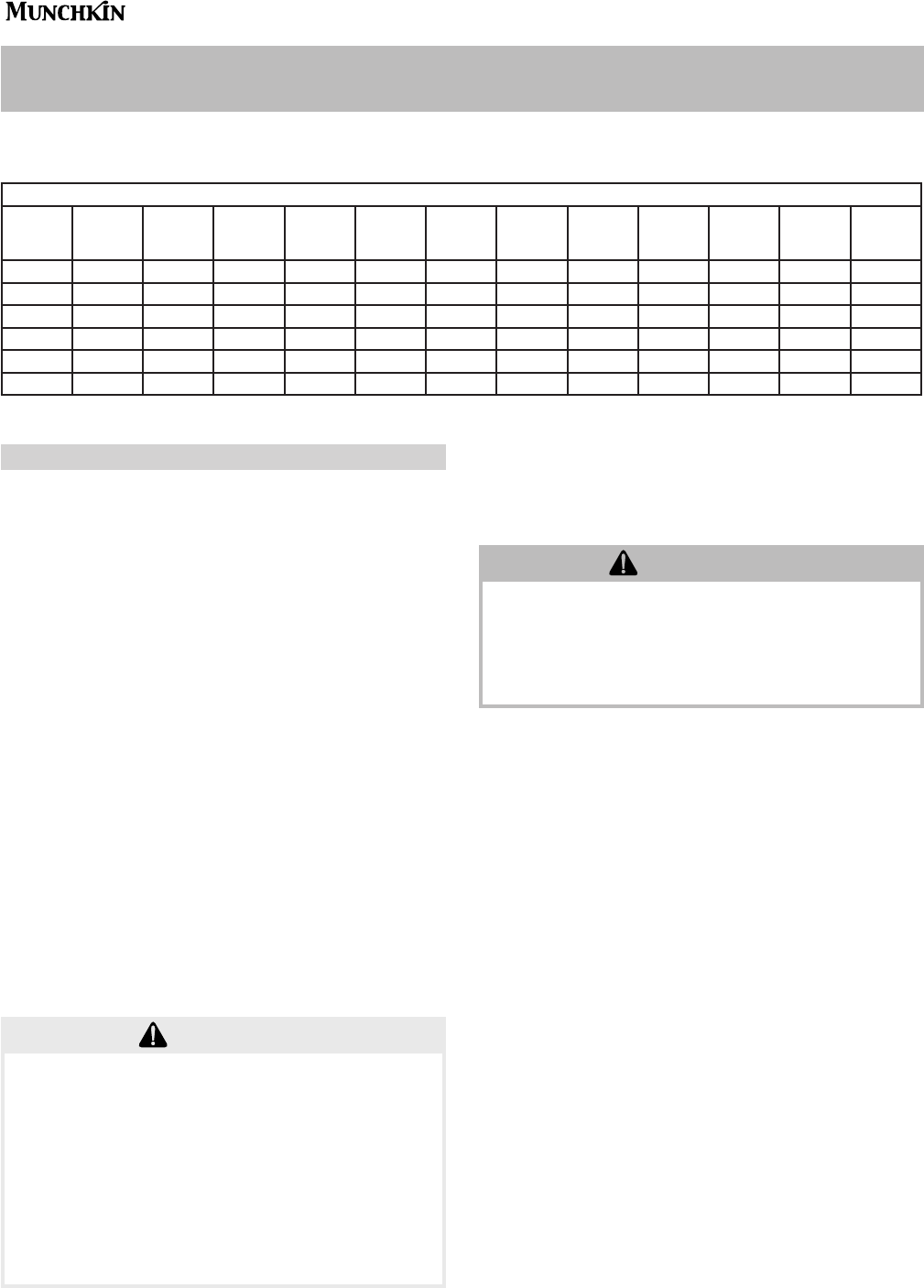
SYSTEM TEMPERATURE RISE CHART
Model
Friction
Feet
20°∆t
Flow
G P M
Friction
Feet
25°∆t
Flow
G P M
Friction
Feet
30°∆t
Flow
G P M
Friction
Feet
35°∆t
Flow
G P M
Friction
Feet
40°∆t
Flow
G P M
Friction
Feet
45°∆t
Flow
G P M
T-50 6.5’ 5 4.5’ 4 3’ 3.3 2’ 2.5 N/A N/R N/A N/R
T-80 7.8’ 8 4.7’ 6.4 2.9’ 5.3 2’ 4.6 1.5’ 4 1’ 3.5
80M 7.8’ 8 4.7’ 6.4 2.9’ 5.3 2’ 4.6 1.5’ 4 1’ 3.5
140M 11’ 14 8’ 11.2 6’ 9.3 4.75’ 8 3.75’ 7 2.5’ 6.2
199M 17’ 19 12.3’ 15.2 8.5’ 12.6 5.75’ 10.8 4’ 9.5 2.5’ 8.4
399M 21’ 39 9’ 31.2 7’ 26 6’ 22.3 5’ 19.5 4’ 17.3
The chart below represents the various system temperatures, their respective flows and friction loss
through the Munchkin which will aid in circulator selection.