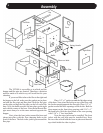
11
Venting
Chimney Connectors and Chimneys
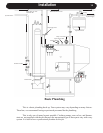
Draft
Draft is widely misunderstood. It is important that you,
the stove operator, realize that draft is a variable effect,
not a given quantity. Stoves and chimneys do not have
draft, yet draft is the key to your stove’s performance.
Draft is a force, produced by an operating stove and
the chimney to which it is attached. It is created by
hot gases rising up the chimney, creating a pressure
difference between the inside of your home and the
outside air. It continually moves fresh combustion air
into the stove, and hot exhaust gases out of the stove;
without this constant ow, the re will go out.
Other factors, such as barometric pressure, winds,
the tightness of the home, the total inside chimney
volume, chimney height and the presence of venting
devices such as exhaust fans also play a role in main-
taining an adequate draft. Low barometric pressures,
super insulated homes, and exhaust fans can reduce
draft; winds can play havoc with draft; and too large or
too small a chimney volume can cause reduced draft
due to the excessive cooling or not enough room to
vent the exhaust gases. Introducing outside air direct-
ly to the stove may help remedy a low draft problem.
Some signs of inadequate draft are smoking, odor,
difculty in maintaining the re, and low heat output.
Overdraft can be caused by a very tall chimney even
if it is the recommended size, and can cause overr-
ing of your stove. Signs of an overdraft include rapid
fuel consumption, inability to slow the re, and parts
of the stove or chimney connector glowing red. It is
important that you follow the chimney guidelines in
this manual, including size, type, and height to avoid
draft problems.
When installed and operated according to this manual,
the appliance will produce enough hot gases to keep
the chimney warm so that adequate draft is maintained
throughout the burn cycle.
Chimney Connectors
In general, following these guidelines will ensure
compliance with all national and provincial codes; prior
to beginning your installation, check with your local
building code ofcial(s) regarding any additional local
requirements or regulations which may inuence the
design and placement of your venting system.
The VF3000 may be installed with (.6 mm) 24 gauge
chimney connector pipe. The size of the connector
should correspond to the size of the ue collar opening.
Do not use makeshift components.
No part of the chimney connector may pass through
an attic or roof space, closet or other concealed space,
or through a oor or ceiling. Whenever possible, avoid
passing the connector through a combustible wall; if you
must, use an approved wall pass-through, described
later in this section.
Assemble the connector beginning at the ue collar,
with the crimped ends pointing towards the stove (to
keep debris and creosote akes inside the system).
Each joint, including the one to the stove’s ue collar
and the one to the chimney itself should be secured
with at least three sheet metal screws. Screws may be
a maximum of 3 inches apart. A 1-1/4" (32 mm) overlap
is required at each joint, including the ue collar attach-
ment. No more than two 90 degree elbows should be
used, and the total length of connector should not ex-
ceed 10 feet (3m) All horizontal runs of connector must
have a minimum upward slope of 1/4" per foot (20 mm
per meter).
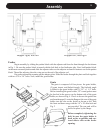
Wall Pass-thrus
Occasionally it is necessary to pass the chimney
connector through a combustible wall to reach the
chimney. Depending on your local building codes, and
the pertinent provincial or national codes, there are
several choices for accomplishing this safely. Before
beginning your installation, contact local ofcials, and
also the chimney connector and chimney manufacturer
for specic requirements.
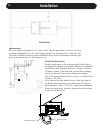
Canada. Three methods are approved by the
Canadian Standards Association. The diagram shows
one method requiring an 18" (460 mm) air space
between the connector and the wall. It allows use of one
or two covers as described in the diagram. The other
two methods are described in detail in the current issue
of CAN/CSA B365, the national standard.
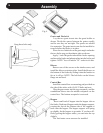
United States In the U.S., the national code is NFPA
211. While many localities adopt this standard, be sure
to check with local authorities before beginning your
installation.
The NFPA (National Fire Protection Association)
permits four methods for passing through a combustible
wall. A commonly used method to pass through a wall
directly to a masonry chimney is to clear a minimum
12"(305 mm) around the entire chimney connector, and
ll it with brick masonry which is at least 3.5"(90 mm)
thick. A reclay liner, minimum 3/8" (9 mm) wall thickness
must run through the brick wall to the chimney liner (but
not beyond the inner surface of the liner). It must be
cemented in place with refractory cement. This method
is illustrated. For details on the other three options, refer
to the most recent edition of the NFPA 211 code.