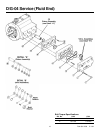
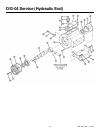
17 D04-991-2400 5/1/04
D/G-04 Troubleshooting
Cavitation
• Inadequate fluid supply because:
— Inlet line collapsed or clogged
— Clogged line strainer
— Inlet line too small or too long
— Air leak in inlet line
— Worn or damaged inlet hose
— Suction line too long
— Too many valves and elbows in inlet line
• Fluid too hot for inlet suction piping system.
• Air entrained in fluid piping system.
• Aeration and turbulence in supply tank.
• Inlet vacuum too high (refer to “Inlet Calculations”, page 3).
Symptoms of Cavitation
• Excessive pump valve noise
• Premature failure of spring or retainer
• Volume or pressure drop
• Rough-running pump
• Premature failure of diaphragms
Drop in Volume or Pressure
A drop in volume or pressure can be caused by one or more of
the following:
• Air leak in suction piping
• Clogged suction line or suction strainer
• Suction line inlet above fluid level in tank
• Inadequate fluid supply
• Pump not operating at proper RPM
• Relief valve bypassing fluid
• Worn pump valve parts
• Foreign material in inlet or outlet valves
• Loss of oil prime in cells because of low oil level
• Ruptured diaphragm
• Cavitation
• Warped manifold from overpressurized system
• O-rings forced out of their grooves from overpressurization
• Air leak in suction line strainer or gasket
• Cracked suction hose.
• Empty supply tank
• Excessive aeration and turbulence in supply tank
• Cavitation
• Abrasives in the fluid
• Valve incompatible with corrosives in the fluid
• Pump running too fast
• Worn and slipping drive belt(s)
• Worn spray nozzle(s)
Pump Runs Rough
• Worn pump valves
• Airlock in outlet system
• Oil level low
• Wrong weight of oil for cold operating temperatures (change
to lighter weight)
• Cavitation
• Air in suction line
• Restriction in inlet/suction line
• Hydraulic cells not primed after changing diaphragm
• Foreign material in inlet or outlet valve
• Damaged diaphragm
• Fatigued or broken valve spring
Premature Failure of Diaphragm
• Frozen pump
• Puncture by a foreign object
• Elastomer incompatible with fluid being pumped
• Pump running too fast
• Excess pressure
• Cavitation
Water (or Process Fluid) in Oil
Reservoir
• Condensation
• Ruptured diaphragm
• Hydraulic cell not properly primed after diaphragm
replacement
• Frozen pump
Strong Water (or Process Fluid)
Pulsations
NOTE: Small pulsations are normal in single-acting pumps
with multiple pumping chambers.
• Foreign object lodged in pump valve
• Loss of prime in hydraulic cell because of low oil level
• Air in suction line
• Valve spring (8) broken
• Cavitation
• Aeration or turbulence in supply tank