308550 13
Operation
Operation of Remote Piloted Pumps
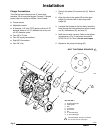
1. Fig. 2 and Parts Drawings. Follow preceding steps
1 through 7 of Starting and Adjusting Pump.
2. Open air regulator (C).
WARNING
The pump may cycle once before the external sig-
nal is applied. Injury is possible. If pump cycles,
wait until end before proceeding.
3. Pump will operate when air pressure is alternately
applied and relieved to push type connectors (14).
NOTE: Leaving air pressure applied to the air motor for
extended periods when the pump is not running may
shorten the diaphragm life. Using a 3–way solenoid
valve to automatically relieve the pressure on the air
motor when the metering cycle is complete prevents
this from occurring.
Pump Shutdown
WARNING
To reduce the risk of serious injury whenever you
are instructed to relieve pressure, always follow the
Pressure Relief Procedure at left.
At the end of the work shift, relieve the pressure.
Maintenance
Lubrication
The air valve is designed to operate unlubricated.
However, if lubrication is desired, every 500 hours of
operation (or monthly) remove the hose from the pump
air inlet and add two drops of machine oil to the air
inlet.
CAUTION
Do not over-lubricate the pump. Oil is exhausted
through the muffler, which could contaminate your
fluid supply or other equipment. Excessive lubrica-
tion can also cause the pump to malfunction.
Flushing and Storage
WARNING
To reduce the risk of serious injury whenever you
are instructed to relieve pressure, always follow the
Pressure Relief Procedure on page 12.
Flush the pump often enough to prevent the fluid you
are pumping from drying or freezing in the pump and
damaging it. Flush with a fluid that is compatible with
the fluid you are pumping and with the wetted parts in
your system. Check with your fluid manufacturer or
supplier for recommended flushing fluids and flushing
frequency.
Always flush the pump and relieve the pressure before
storing it for any length of time.
Tightening Threaded Connections
Before each use, check all hoses for wear or damage,
and replace as necessary. Check to be sure all
threaded connections are tight and leak free. Check
fasteners. Tighten or retorque as necessary. Although
pump use varies, a general guideline is to retorque
fasteners every two months. See Torque Sequence,
page 32.
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
Establish a preventive maintenance schedule, based
on the pump’s service history. This is especially impor-
tant for prevention of spills or leakage due to dia-
phragm failure.