111044-01D
For more information, visit www.desatech.com
For more information, visit www.desatech.com
5
5
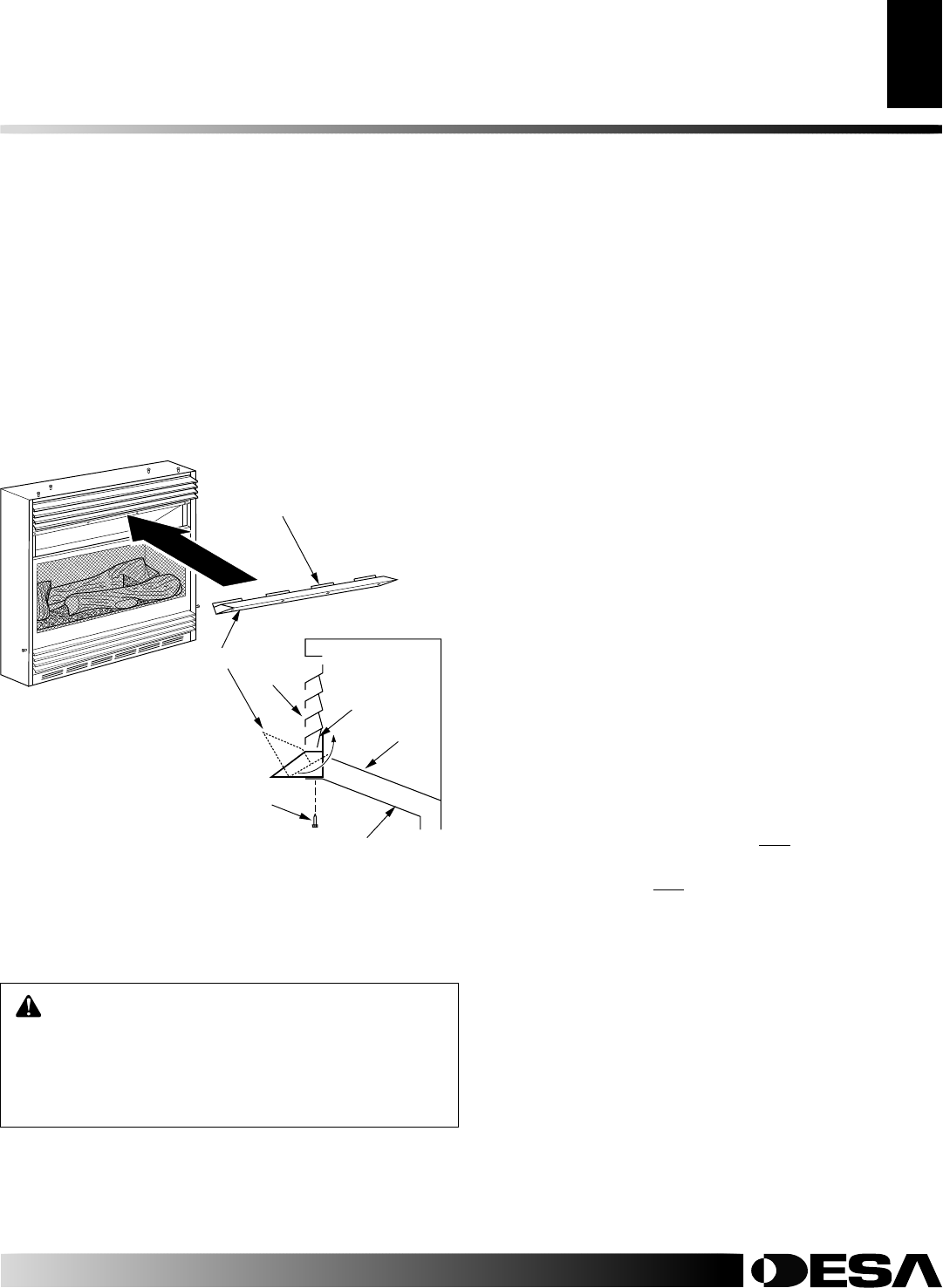
Figure 4 - Assembling Hood
Hood Tab
Assembling Hood
1. Locate four black phillips sheet metal screws from the hard-
ware packet.
2. Rotate hood as shown in Figure 4. Make sure hood tabs
point toward fireplace.
3. Insert hood tabs between baffle and louvers (see Figure 4).
4. Gently rotate hood to upright position. Make sure hood tabs are
behind louvers and hood is resting on firebox top (see Figure 4).
5. Align screw holes on hood with screw holes on firebox top.
6. Insert screws as shown in Figure 4. Tighten screws firmly.
Sheet Metal
Screws
Louver
Baffle
Firebox Top
Hood
Hood Tabs
ASSEMBLY
Continued
AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND
VENTILATION
Today’s homes are built more energy efficient than ever. New materi-
als, increased insulation, and new construction methods help reduce
heat loss in homes. Home owners weather strip and caulk around
windows and doors to keep the cold air out and the warm air in. During
heating months, home owners want their homes as airtight as possible.
WARNING: This heater shall not be installed in a
confined space or unusually tight construction un-
less provisions are provided for adequate combus-
tion and ventilation air. Read the following instruc-
tions to insure proper fresh air for this and other fuel-
burning appliances in your home.
While it is good to make your home energy efficient, your home
needs to breathe. Fresh air must enter your home. All fuel-burning
appliances need fresh air for proper combustion and ventilation.
Exhaust fans, fireplaces, clothes dryers, and fuel burning appliances
draw air from the house to operate. You must provide adequate fresh
air for these appliances. This will insure proper venting of vented
fuel-burning appliances.
PROVIDING ADEQUATE VENTILATION
The following are excerpts from National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54, Section 5.3, Air for Combustion and Ventilation.
All spaces in homes fall into one of the three following ventilation
classifications:
1. Unusually Tight Construction
2. Unconfined Space
3. Confined Space
The information on pages 5 through 7 will help you classify your
space and provide adequate ventilation.
Unusually Tight Construction
The air that leaks around doors and windows may provide enough
fresh air for combustion and ventilation. However, in buildings of
unusually tight construction, you must provide additional fresh air.
Unusually tight construction is defined as construction
where:
a. walls and ceilings exposed to the outside atmosphere
have a continuous water vapor retarder with a rating
of one perm (6 x 10
-11
kg per pa-sec-m
2
) or less with
openings gasketed or sealed
and
b. weather stripping has been added on openable win-
dows and doors
and
c. caulking or sealants are applied to areas such as
joints around window and door frames, between sole
plates and floors, between wall-ceiling joints, between
wall panels, at penetrations for plumbing, electrical,
and gas lines, and at other openings.
If your home meets all of the three criteria above, you
must provide additional fresh air. See
Ventilation Air
From Outdoors
, page 7
.
If your home does not meet all of the three criteria above,
proceed to
Determining Fresh-Air Flow For Fireplace
Location
, page 6.
ASSEMBLY
Assembling Fireplace (Cont.)
AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION
Providing Adequate Ventilation


















