128
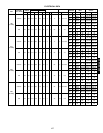
ELECTRICAL DATA (cont)
L
EGEND
*Heater capacity (kW) is based on heater voltage of 208 v, 240 v, 480 v, and
600 v. Heaters are rated at 240 v, 480 v, or 600 v. If power distribution voltage to
unit varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will vary accordingly. To deter-
mine heater capacity at actual unit voltage, multiply 240 v, 480 v, or 600 v capac-
ity by multipliers found in table on page 110.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements for multimotor and combination load
equipment (refer to NEC Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective
device for the unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker. The Canadian units may
be fuse or circuit breaker.
2.
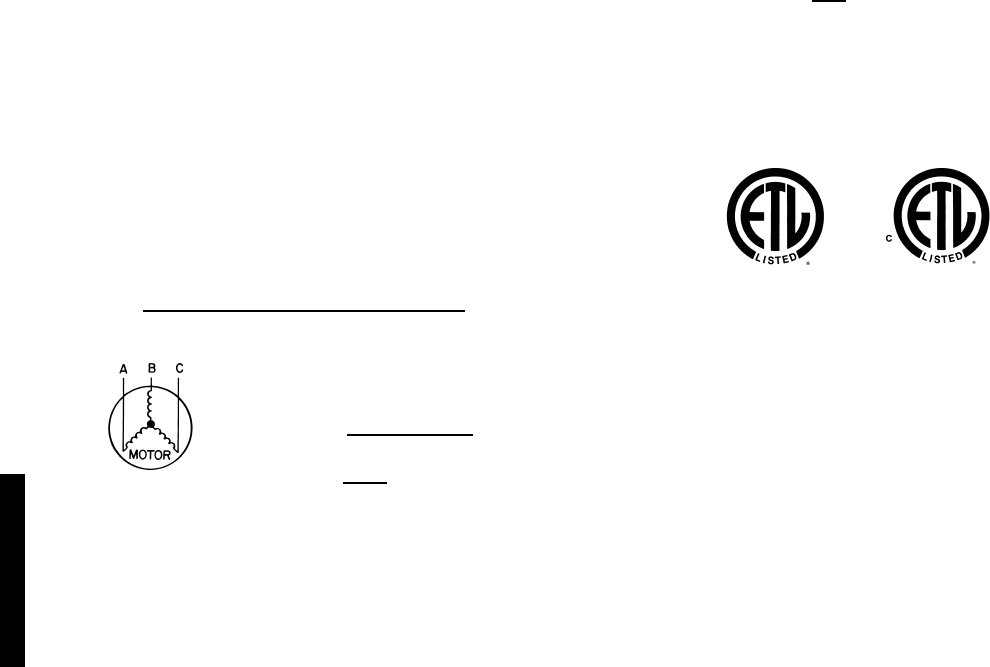
Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater
than 2%.
Use the following formula to determine the percent of voltage
imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
EXAMPLE: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance.
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum
allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT:
If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%, con-
tact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. MCA calculation for 559F180-300 units with electric heaters over 50 kW =
(1.25 x IFM amps) + (1.00 x heater FLA).
FLA —
Full Load Amps
HACR —
Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM —
Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA —
Locked Rotor Amps
MCA —
Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP —
Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC —
National Electrical Code
OFM —
Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA —
Rated Load Amps
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
452 + 464 + 455
3
=1371
3
= 457
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
457
0TFQ004-012
559F180-300