DCP200 Profile Controller & Recorder - Product Manual
51-52-25-150, Issue 1 – April 2009 Glossary Page 145
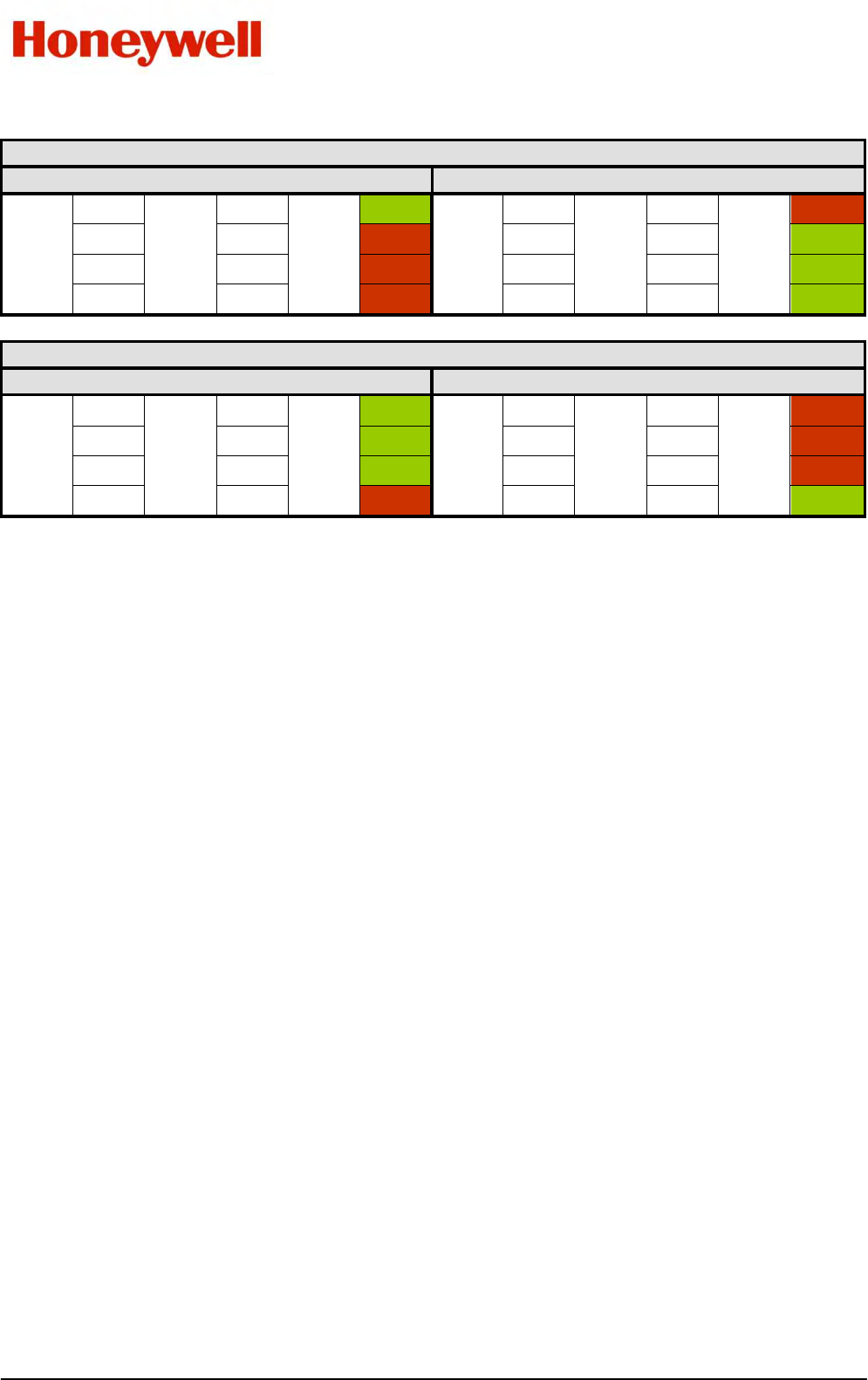
Table 28. Examples Of Logical Alarm Outputs
Logical OR: Alarm 1 OR Alarm 2
ALARM 1
OFF
ALARM 2
OFF
OUTPUT
OFF
ALARM 1
OFF
ALARM 2
OFF
OUTPUT
ON
ON OFF ON ON OFF OFF
OFF ON ON OFF ON OFF
ON ON ON ON ON OFF
Logical AND: Alarm 1 AND Alarm 2
ALARM 1
OFF
ALARM 2
OFF
OUTPUT
OFF
ALARM 1
OFF
ALARM 2
OFF
OUTPUT
ON
ON OFF OFF ON OFF ON
OFF ON OFF OFF ON ON
ON ON ON ON ON OFF
Loop Alarm
A loop alarm detects faults in the control feedback loop, by continuously monitoring process
variable response to the control output(s). If one of the 5 alarms is defined to be a loop
alarm, it repeatedly checks if the PID control output is at saturation. If saturation is reached
(0% or 100% power for single control type, -100% or +100% for dual control type), an internal
timer is started. Thereafter, if the output has not caused the process variable to be corrected
by a predetermined amount 'V' after time 'T' has elapsed, the alarm becomes active.
Subsequently, the alarm repeatedly checks the process variable and the PID output. When
the process variable starts to change value in the correct sense or when the PID output is no
longer at the limit, the alarm is deactivated.
For PID control, the loop alarm time 'T' can be automatic (twice the Integral Time value) or
set to a user defined value. Correct operation with the automatic loop alarm time depends
upon reasonably accurate PID tuning. The user defined value is always used for On-Off
control, and the timer starts as soon as an output turns on.
The value of 'V' is dependent upon the input type. For Temperature inputs, V = 2°C or 3°F.
For Linear inputs, V = 10 x LSD
The loop alarm is automatically disabled during manual control mode and during execution of
a Pre-Tune. Upon exit from manual mode or after completion of the Pre-Tune routine, the
loop alarm is automatically re-enabled.
Also refer to: Alarm Types, Control Type, Manual Loop Alarm Time, Linear Input, LSD,
Manual Mode, On-Off Control, PID, Pre-Tune, Process Variable and Tuning.
LSD
The Least Significant Digit (LSD) is the smallest incremental value that can be shown at the
defined display resolution.
Also refer to: Display Resolution.
mADC
This stands for milliamp DC. It is used in reference to the linear DC milliamp input ranges and
the linear DC milliamp outputs. Typically, these will be 0 to 20mA or 4 to 20mA.
Also refer to: Input Range, Linear Input, Linear Output,, mVDC, Process Variable and VDC
