SECTION 2 HOW YOUR WATER SOFTENER WORKS
I
2B. SOFT WATER SERVICE AND REGENERATION
SERVICE
When the softener is giving you soft water, it is
called "Service". During service, hard water comes
from the house main water pipe into the softener.
Inside the softener resin tank is a bed made up of
thousands of tiny, plastic resin beads (FIG. 4). As
hard water passes through the bed, each bead
attracts and holds the hardness minerals. This is
called ion-exchanging. It is much like a magnet
attracting and holding metals. Water without the
hardness minerals (soft water) flows out of the
softener and into the house soft water pipes.
After a period of time, the resin beads hold all of the
hardness minerals they can, and cleaning with salt
brine is needed. This cleaning is called regenera-
tion or recharge. Regeneration is started at 2:00
a.m. by the electronic timer (see page 14). It takes
place in 5 stages or cycles. These are:
FT] FILL
[] BRINING
F] BRINE RINSE
r-_ BACKWASH
r_ FAST RINSE
NOTE:
If the Clean feature is set to ON, additional
backwash and fast rinse cycles occur before the fill
cycle.
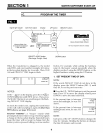
WATER FLOW THROUGH THE
SOFTENER IN SERVICE
salt storage
tank (salt .
not shown) _'
brine valve
soft water
OUT IN
hard water
resin tank
resin bed
REGENERATION
[] FILL: Salt, dissolved in water, is called brine.
Brine is needed to clean the hardness minerals
from the resin beads. To make the brine, water
flows into the salt storage area during the fill stage
as shown in FIG. 5. Fill cycle length depends on
how much soft water making capacity you have
used since the last regeneration. As you use more
water, fill time increases so more brine is made. The
greater amount of brine cleans more hardness
minerals from the resin bed.
WATER FLOW THROUGH THE
SOFTENER IN FILL
salt storage
tank -...
-j
brine valve
\\\\\\
soft water hard water
OUT IN
q
,
\
fillwater
12