20 TRG-TRC012-EN
notes
period two
Refrigeration Cycle
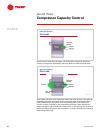
Today the most commonly used refrigerant in helical-rotary chillers is HCFC-22.
Due to the scheduled phaseout of HCFC-22, most helical-rotary chillers will be
redesigned using HFC refrigerants. Many challenges are encountered when
redesigning a chiller to use a refrigerant with different thermodynamic
characteristics. This is due to the different efficiency, capacity, and operating
pressure characteristics of each of the refrigerants.
Take a closer look at each of these issues by examining the effects of using
different refrigerants in the same helical-rotary chiller designed for use with
HCFC-22.
■ Efficiency – In order to meet today’s high standards of energy efficiency,
chillers using refrigerants with a lower thermal efficiency, such as HFC-404a and
HFC-410a, will require larger heat exchangers and more efficient compressors.
These changes add to the product cost and increase the physical size of the
chiller.
■ Capacity – HFC-134a has a lower capacity compared to HCFC-22, which
means more refrigerant needs to be pumped through the chiller to achieve the
same capacity. This can be accomplished by using a larger compressor or
increasing the speed of the compressor. Both tend to increase product cost and
design complexity. On the other hand, HFC-410a has a higher capacity
compared to HCFC-22, which means less refrigerant needs to be pumped
through the chiller to achieve the same capacity. The advantage is that smaller,
less expensive compressors can be used.
■ Operating Pressure – A refrigerant that operates at a higher pressure
requires heat exchangers and pressure vessels to be designed for the higher
pressure. This adds cost. Conversely, higher pressure refrigerants have a
greater density. As density increases, the required amount of refrigerant
decreases, meaning that smaller or slower-speed compressors can be used.
Lower pressure refrigerants, such as HFC-134a, will require larger or higher-
speed compressors in order to achieve the same capacity as a similar chiller
using HCFC-22.
0
0
20
20
40
40
60
60
80
80
100
100
120
120
140
140
160
160
HCFC-22
HCFC-22
HFC-134a
HFC-134a
HFC-404a
HFC-404a
HFC-407c
HFC-407c
HFC-410a
HFC-410a
efficiency
efficiency
capacity
capacity
pressure
pressure
refrigerants…
Thermodynamic Characteristics
percent
percent
Figure 30