14
1. Size and install the gas supply piping properly in
order to provide a supply of gas sufficient to meet
the maximum demand without undue loss of
pressure between the meter and the boiler.
2. Determine the volume of gas to be provided to the
boiler in cubic feet per hour. To obtain this value,
divide the Btu per hour rating (on the boiler rating
plate) by the heating value of the gas in Btu per
cubic feet. Obtain the heating value of the gas from
the gas supplier. As an alternative, use Table 5.1, 5.2
or 5.3 on the next page to obtain the volume of gas
to be provided to the boiler.
3. Use the value obtained above as the basis for piping
sizing. Size the gas piping in accordance with Table
5.4. Consult the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1/NFPA 54 and/or CAN/CSA B149.1, Natural
Gas and Propane Installation Code for proper sizing
options.
4. Locate the drop pipe adjacent to, but not in front of
the boiler.
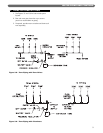
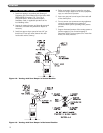
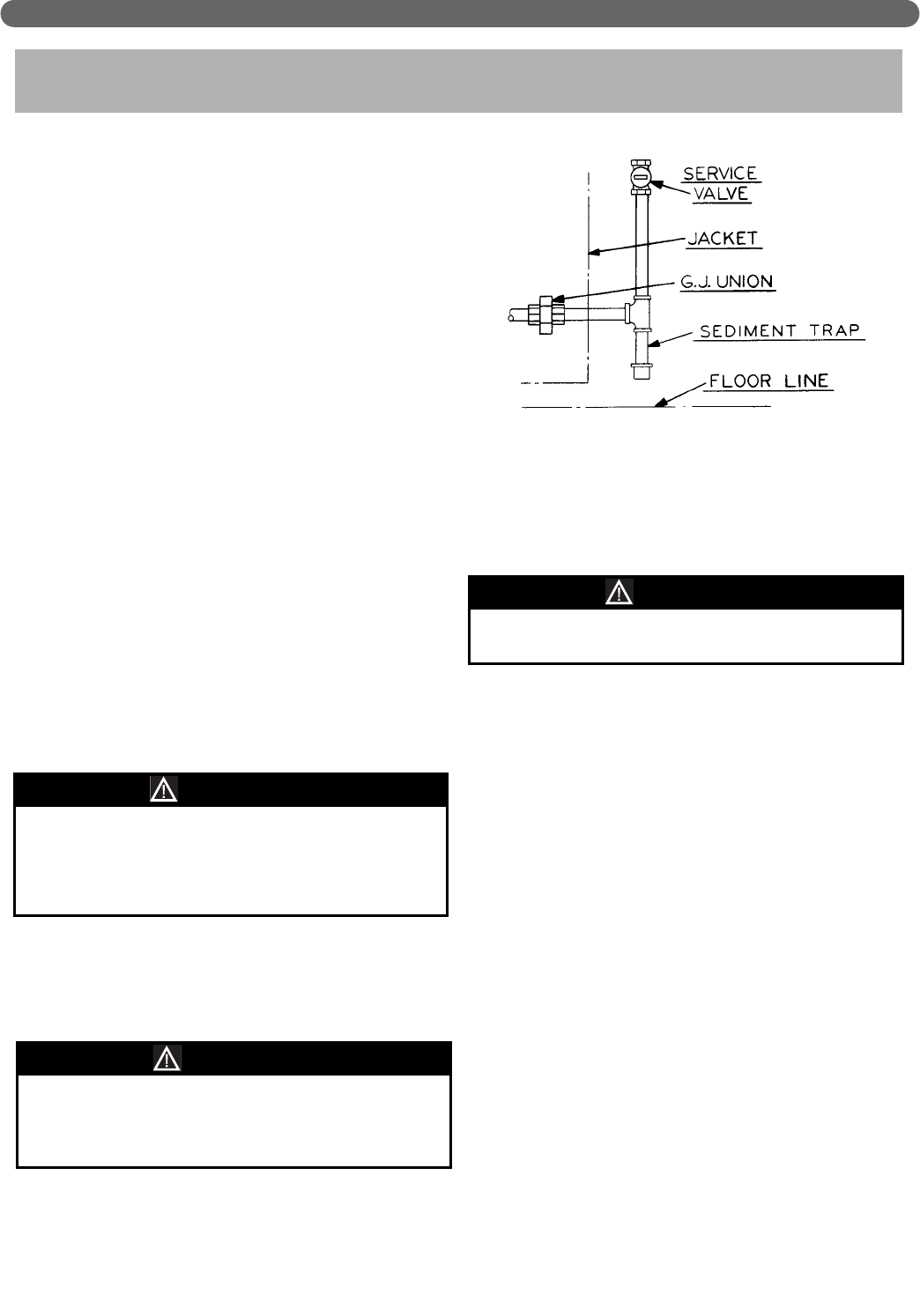
5. Install a sediment trap. See Figure 5.1. Locate a tee
in the drop pipe at same elevation as the gas inlet
connection to the boiler. Extend the drop pipe to a
pipe cap.
6. Install a ground joint union ahead of the gas control
assembly to permit servicing of the control. Some
local codes require an additional service valve when
using the combination gas controls. If your code
requires such a valve, a suggested location is shown
in Figure 5.1.
7. Check piping for leaks.
Use an approved gas detector, a non-corrosive leak
detection fluid or other leak detection method. If
leaks are found, turn off all gas flow and repair as
necessary.
8. Disconnect the boiler and its individual shut-off valve
from the gas supply piping system during any
pressure testing of that system at test pressure in
excess of 1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
Isolate the boiler from the gas supply piping system
by closing its individual service valve during any
pressure testing of the gas supply piping system at
test pressure equal to or less than 1/2 psig (3.5 kPa).
9. Minimum permissible supply pressure for purposes of
input adjustment:
MI-09 Standing Pilot
Natural Gas 5.2″ WC (1.3 kPa)
All other MI/MIH
Natural Gas 5.0″ WC (1.2 kPa)
All MI LP Gas 11.0″ WC (2.7 kPa)
Maximum permissible supply pressure to the boiler:
All MI/MIH Natural Gas 13.5″ WC (3.5 kPa)
All MI LP Gas 13.5″ WC (3.5 kPa)
5. GAS PIPING
Figure 5.1: Gas Connection to Boiler
When checking for leaks, do not use matches,
candles, open flames or other methods that provide a
source of ignition.This can ignite a gas leak,
resulting in fire or explosion.
WARNING
Use a pipe joint sealing compound that is resistant to
the action of liquefied petroleum gas. A non-resistant
compound may lose sealing ability in the presence of
this gas, resulting in a gas leak and fire or explosion
potential.
WARNING
Do not subject the gas valve to more than 1/2 psi (3.5
kPa) pressure. Doing so may damage the valve.
CAUTION
GAS PIPING