5
W415-0297 / D / 04.03.03
ROOM 2
ROOM 1
This heater shall not be installed in a confined space or
unusually tight construction unless provisions are pro-
vided for adequate combustion and ventilation air.
In order to avoid the possibility of exposed insulation
or vapour barrier coming in contact with the fireplace
body, it is recommended that the walls of the fireplace
enclosure be 'finished', (i.e. drywall/sheetrock) as would
any other outside wall of the home. This will ensure
that clearance to combustibles is maintained within the
cavity.
The National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 defines a con-
fined space as a space whose volume is less than 50
cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour (4.8 m
3
per kW) of the
aggregate input rating of all appliances installed in that
space and an unconfined space as a space whose vol-
ume is not less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour
(4.8 m
3
per kW) of the aggregate input rating of all appli-
ances installed in that space. Rooms communicating di-
rectly with the space in which the appliances are installed,
through openings not furnished with doors are consid-
ered a part of the unconfined space.
The GVF36 is rated at 30,000BTUs per hour and
therefore requires a minimum unconfined space
of 1,500 cubic feet.
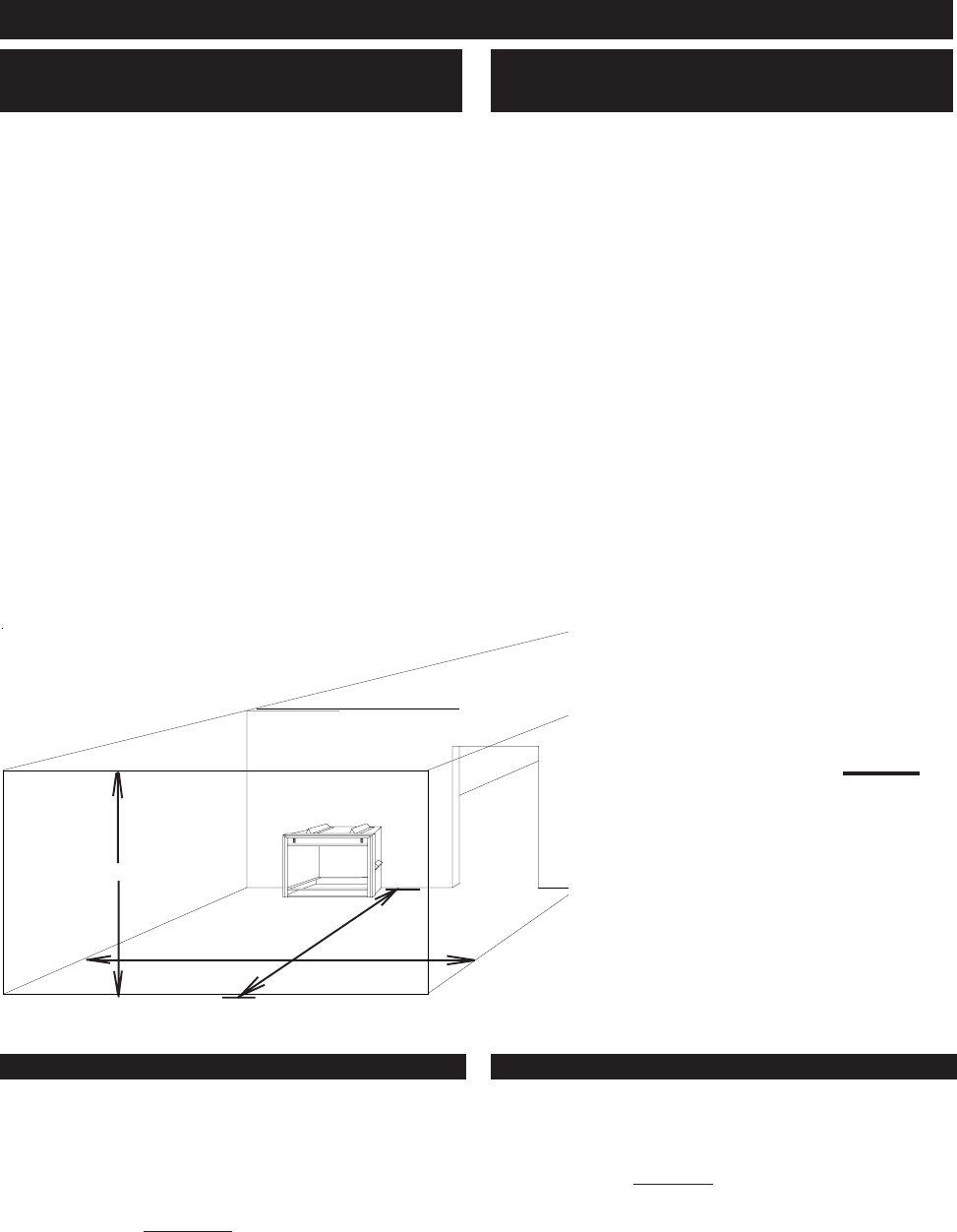
To determine the volume of the room where the heater is
to be installed, multiply the width x the length x the ceiling
height of that room measured in feet. If any adjoining rooms
are connected by grills or openings such as kitchen pass-
throughs, etc., the volume of those rooms may be added to
the total.
Multiply the room volume by 1000 and divide this amount
by 50 to determine the maximum Btu/hr that the space can
support with adequate combustion and ventilation air.
Add the Btu/hr of all fuel burning appliances located within
the space such as gas furnace, gas water heater, etc. Do
not include direct vent gas appliances which draw their
input and output air from and to the outdoors.
WARNING: If the area in which the heater may be oper-
ated is smaller than that defined as an unconfined space
or if the building is of unusually tight construction, provide
adequate combustion and ventilation air by one of the
methods described in the National Fuel Gas Code ANSI
Z223.1, Section 5.3 or the applicable local code.
FIGURE 1
Room Volume = Length x Width x Height
Max BTU/hr = Room Volume x 1000 ÷ 50
If for example,
the length of the rooms is 10 feet,
the width of Room 1 is 10 feet,
the width of Room 2 is 15 feet
the height of the rooms is 8 feet.
The volume of Room 1: 10 x 10 x 8 = 800 cubic feet.
The volume of Room 2: 10 x 15 x 8 = 1200 cubic feet.
If in this example a solid door separates Room 1 from
Room 2, the volume of Room 2 could not be used. In this
case the maximum BTU/h would be:
Maximum BTU/h:
800 x 1000
= 16,000 BTU/h
This would be considered a confined space since it can
not support the 30,000BTU/h input of the heater and it
would be necessary to provide adequate combustion and
ventilation air to Room 1.
In this example, because there is no door to the adjoining
room, the volume of the adjoining room may be added to
the volume of the room with the heater to get a total
unconfined space.
The total unconfined space: 800 + 1200 = 2000 cubic feet.
Maximum BTU/h:
2000 x 1000
= 40,000 BTU/h
If there are no more fuel burning appliances within this
space then the 30,000 BTU/h input of the fireplace is suit-
able to be installed. This also assumes that the construc-
tion of this space is not unusually tight.
HEIGHT
WIDTH
LENGTH
50
50
INSTALLATION
COMBUSTION & VENTILATION
AIR PROVISIONS
DETERMINING CONFINED OR
UNCONFINED SPACE
EXAMPLE 1 EXAMPLE 2


















