Calculating the Battery Size Power Supply Calculations
MS-2/MS-4 PN 51512:E 01/18/05 47
5.4 Calculating the Battery Size
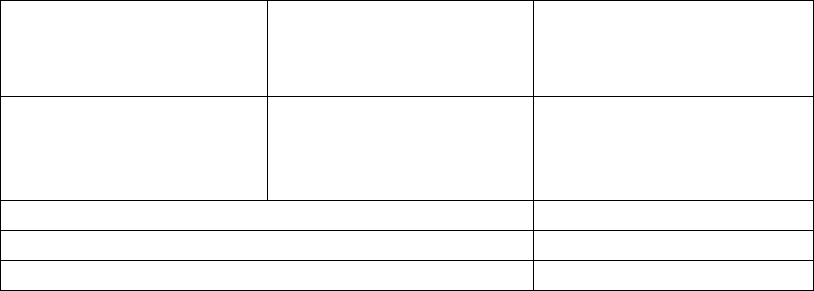
Use Table 5-4 to calculate the total Standby and Alarm load in ampere hours (AH).
This total load determines the battery size (in AH), required to support the control panel
under the loss of AC power. Complete Table 5-4 as follows:
1. Enter the totals from Table 5-3 on page 46, Calculation Columns 2 and 3 where
shown
2. Enter the NFPA Standby and Alarm times (refer to ‘NFPA Requirements’
below)
3. Calculate the ampere hours for Standby and Alarm, then sum the Standby and
Alarm ampere hours
4. Multiply the sum by the derating factor of 1.2 to calculate the proper battery size
(in AH)
5. Write the ampere hour requirements on the Protected Premises label located
inside the cabinet door
5.4.1 NFPA Battery Requirements
• NFPA 72 Local, Central and Proprietary Fire Alarm Systems require 24 hours of
standby power followed by 5 minutes in alarm
• NFPA 72 Auxiliary and Remote Station require 60 hours of standby followed by
5 minutes in alarm. Batteries installed in a system powered by a generator need
to provide at least 4 hours of standby power
5.4.2 Selecting and Locating Batteries
Select batteries that meet or exceed the total ampere hours calculated in Table 5-4 . The
control panel can charge batteries in the 7 AH to 18 AH range. The control panel cabi-
net is capable of housing batteries up to 7 AH. Batteries larger than 7 AH require the
BB-17F or other UL listed external battery cabinet.
TABLE 5-4:Total Secondary Power Requirements at 24 VDC
Secondary Standby Load
(total from Table 5-3 Calculation
Column 3)
[ ]
Required Standby Time
(24 or 60 hours)
X[ ] = AH
Primary Alarm Load
(total from Table 5-3 Calculation
Column 2)
[ ]
Required Alarm Time
(for 5 min., enter 0.084,
for 10 min., enter 0.168)
X[ ]
= AH
Sum of Standby and Alarm Ampere Hours = AH
Multiply by the Derating Factor X 1.2
Battery Size, Total Ampere Hours Required = AH


















