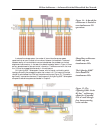
In a shared bus storage system, the number of internal simultaneous processor
operations that can occur is equal to the number of buses on the backplane. The shared
buses are used by all host channels to communicate between the processors on the host
adapters and cache memory. In the case of the shared-bus design shown in Figure 14, there
are four separate buses for data and control information. Therefore a maximum of at most
four I/Os can be processed simultaneously in this architecture.
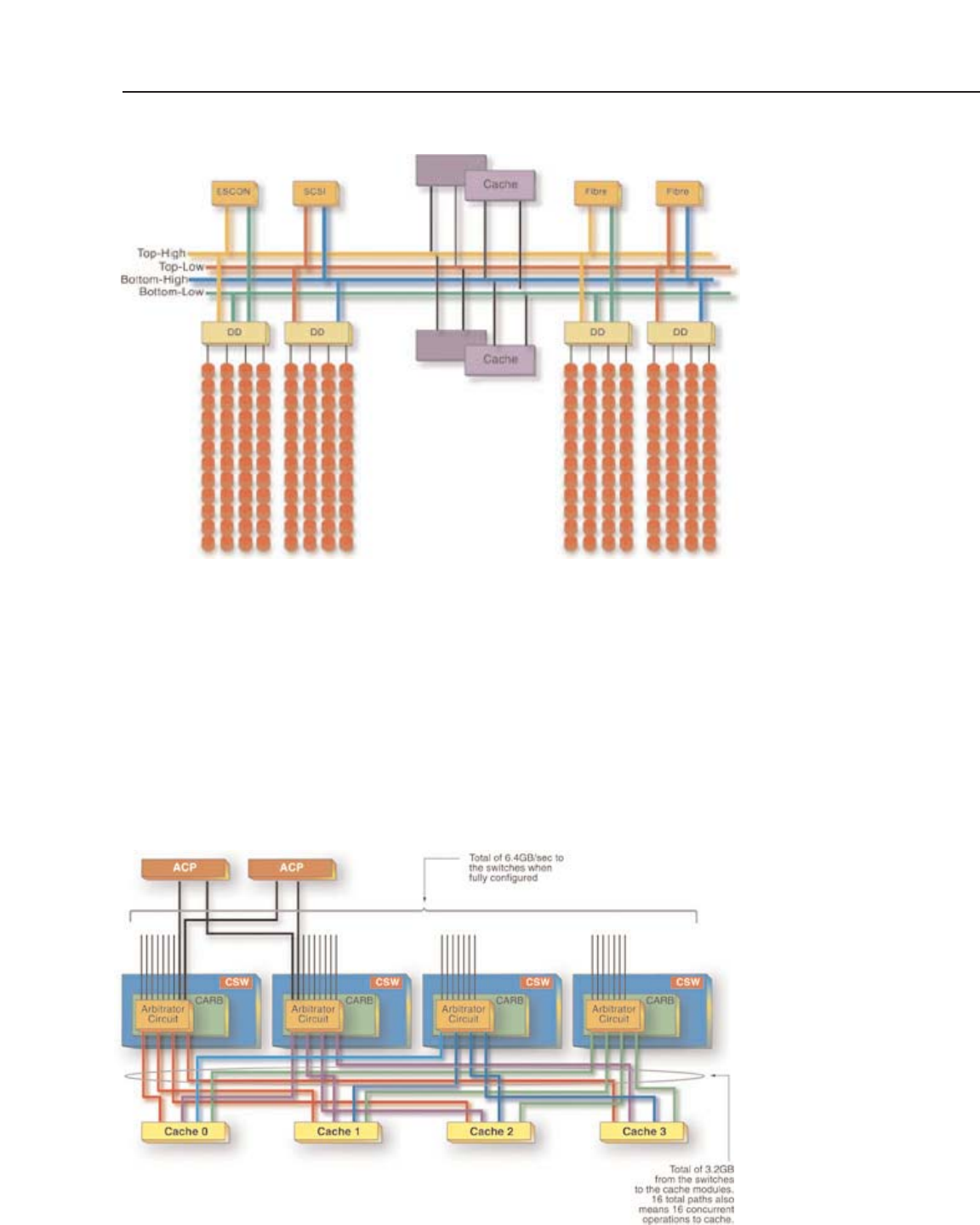
On Lightning 9900
™
Series system, however, with its internal non-blocking switch
topology connecting the processors to cache, that number is 16. This is equal to the total
number of paths between the CSW and the cache module ports (Figure 15). This results in
significantly improved simultaneous I/O performance of the Lightning 9900
™
Series system
compared to shared-bus systems as discussed in Chapter 8.
Figure 14 – A shared-bus
architecture is limited to
two simultaneous I/O
operations.
Shared-bus architecture
handle only two
simultaneous I/Os.
The Lightning 9900
™
Series handle 16
simultaneous I/Os.
Figure 15 –The
Lightning 9900
™
Series
Hi-Star
™
architecture
allows for 16 parallel
I/Os to cache through
four interconnecting
cache switches.
17
Hi-Star Architecture – An Internal Switched Hierarchical Star Network