The Cache Switch Provides Non-blocking Switched Access to Cache
At the heart of the C-HSN is the Cache Switch (CSW). Together, these four switches
(in the 9960) form the internal start using parallel switch fabric bus (PSFB) of the C-HSN.
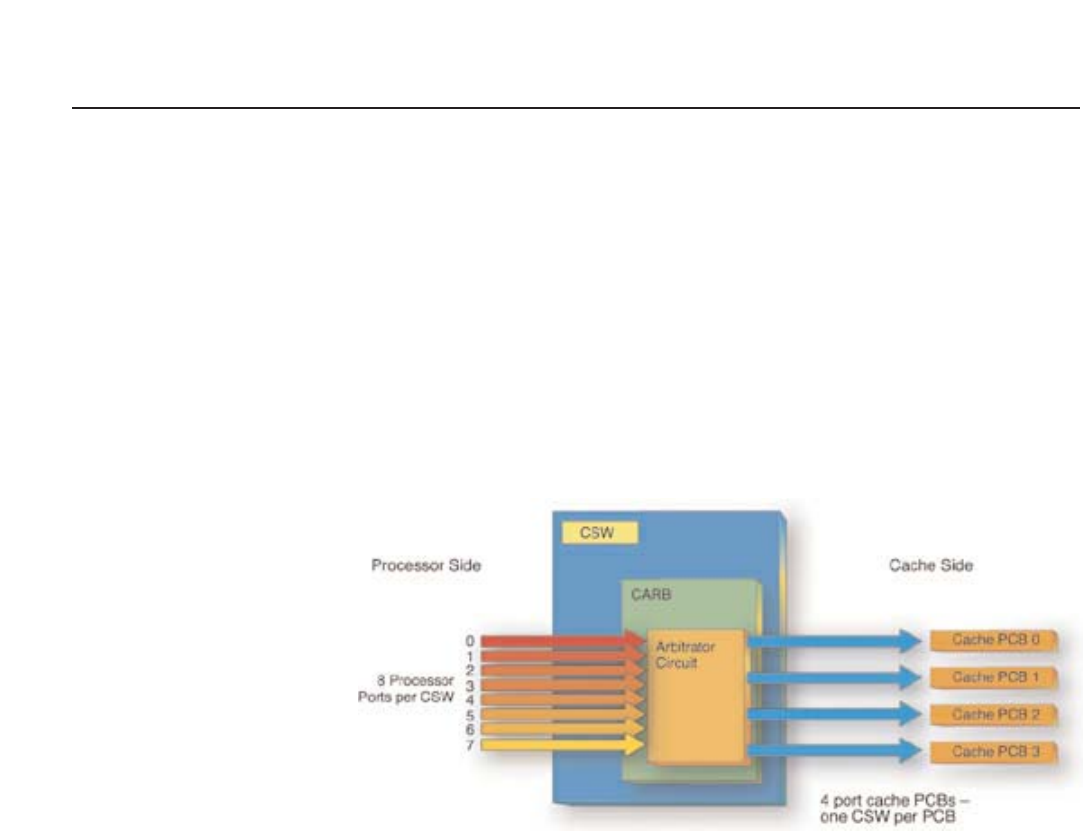
The CSW is a specially designed crossbar switch that functions as a combination MUX,
path arbitrator, and non-blocking network switch. The CSW functions as a MUX by
supporting eight paths into the processor side of each switch and four paths to the cache
modules (8 to 4 routing). All total, there are 32 paths at the processor side of the fabric
network and 16 paths to the cache modules from the cache side of the fabric network.
As shown in Figure 13, Cache Memory Arbitrator (CARB) allows the CSW to act as an
arbitrator, handling the access and addressing to and from the cache modules. The CSW
also manages the non-blocking paths between the processors to and from the cache.
The Path Bandwidth Between the CSW and CHIPs or ACPs is 6.4GB/sec
The paths that connect the Client Host Interface Processors, or CHIPs (through the
Data Adapters – DTA) to the CSW and the CSW to the cache modules are each 16 bits
wide, plus 2 bits for parity. The bandwidth of each path is 200MB/sec. This is the data
transfer rate of a 16-bit wide path (parallel) clocked at 100MHz (16 bits at 100MHz equals
200MB/sec). As mentioned, there are 32 paths from the processor modules of the
Lightning 9960
™
(ACPs and CHIPs) to the ports of the CSWs. This equals 6.4GB/sec
(32 paths at 200MB/sec) of bandwidth to the processor side of the switched fabric (when
all 16 component modules are installed).
The Path Bandwidth Between the CSW and the Cache Adapters (CAs)
is 3.2GB/sec
The bandwidth between the cache side of the Cache Switch (CSW) and the cache
modules is 3.2GB/sec (16 paths at 200MB/sec) total. This bandwidth will always be
3.2GB/sec as long as the four CSWs and the four cache modules are installed and
functioning.
Advantages of a Switched Architecture Compared to a Shared Bus
Architecture
When considering the advantages of a switched bus architecture to that of a shared bus
architecture (Figure 14), the number of operations that can be present on the buses
simultaneously is the key difference.
The CSW is at the heart
of the Lightning 9900
™
Series.
Figure 13 – The CSW
and CARBs provide
non-blocking channel
access to all cache.
Hitachi Data Systems
16