WATER SOFTENER START-UP
SECTION 1
9
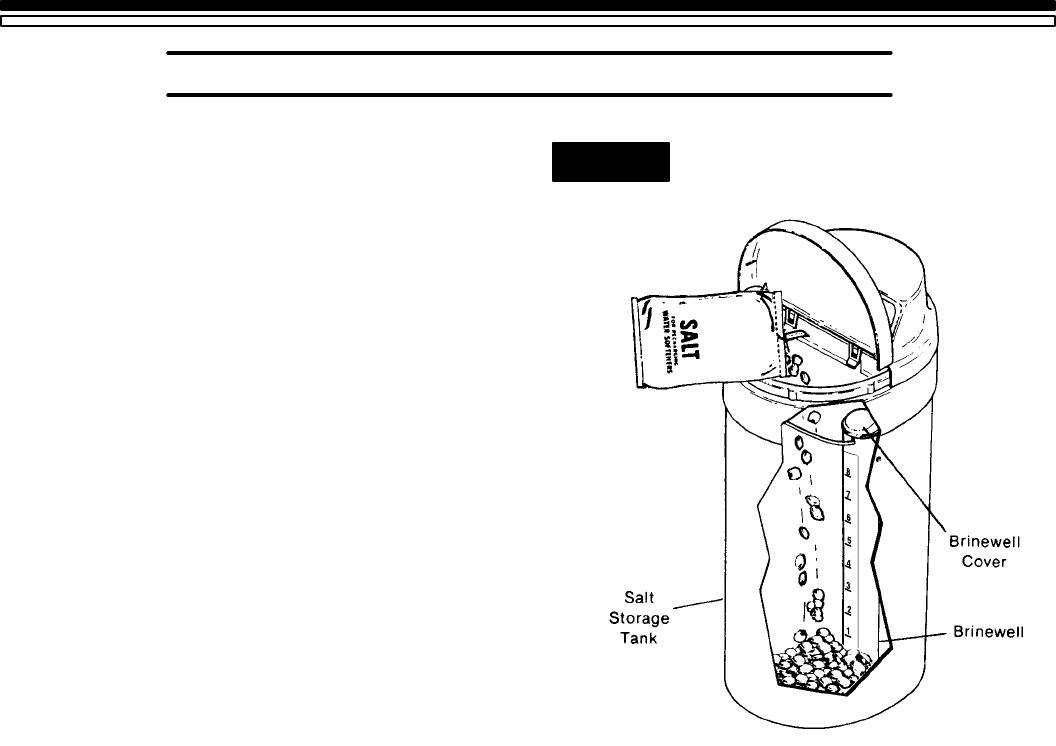
1E. FILL THE STORAGE TANK WITH SALT
Brine (salt dissolved in water) is needed for each and
every regeneration. The water for making brine is
metered into the salt storage tank by the softener.
However, you must keep the tank filled with salt.
Fill the tank with NUGGET or PELLET water softener
salt. DO NOT use rock salts, as they have dirt and
sediments that will stop the softener from working.
Before filling, be sure the brinewell cover is in place
on the top of the brinewell. Salt storage capacity is
shown on page 19. Be sure to set the salt monitor
system (see page 10).
NOTES:
The salt monitor system (page 10) is calibrated to the
density of nugget or pellet water softener salt. The
monitor will not work as accurately with other types
of salt including rock and solar.
In humid areas, it is best to fill the storage tank
halfĆfull, and to refill it more often. Salt bridging (see
page 15) occurs more often when conditions are
humid.
WATER SOFTENING SALT WITH IRON REMOV-
ING ADDITIVES — Some salts have an additive to
help the softener handle iron in the water supply.
Although this additive may help to keep the softener
resin clean, it may also release corrosive fumes that
will weaken and shorten the life of some softener
parts.
FIG. 3 ADD SALT
Sodium information: Water softeners using sodium
chloride for regeneration add sodium to the water.
Persons who are on sodium restricted diets should
consider the added sodium as part of their overall
sodium intake.
For example, if your water supply is 15 grains hard,
you would have to drink 3 quarts of softened water
to consume 335 milligrams of sodium. That is
equivalent to eating 2Ć1/2 slices of white bread.
Persons who are concerned about their drinking
water should consider a Kenmore Drinking Water
System that will remove or reduce in excess of 90% of
the sodium and other drinking water contaminants.
You have now finished the water softener start up. After the sanitizing recharge, on
page 8, the softener will be giving you soft water.