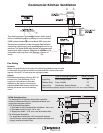
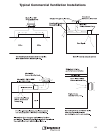
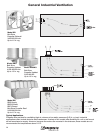
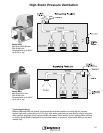
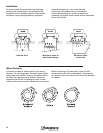
In a steady-state system, as the fan rpm changes, cfm, Ps
and BHp (horsepower) also change. The equations below,
known better as fan laws, show the relationship between
these performance parameters.
cfm
New
=
rpm
New
x cfm
Old
rpm
Old
Ps
New
=
(
rpm
New
)
2
x Ps
Old
rpm
Old
Bhp
New
=
(
rpm
New
)
3
x Bhp
Old
rpm
Old
The first two equations have already been covered in the fan
and system dynamics section. Refer to the examples in those
sections on how to apply these equations.
The third equation relates horsepower to rpm. The change in
horsepower can be determined when the rpm is increased by
25%. This is shown below:
Bhp
New
= (1.25)
3
x Bhp
Old
= 1.95 x Bhp
Old
NOTE: a 25% increase in rpm results in a 95% increase in
horsepower. Considering this, initial fan selections should be
sized with motor horsepowers greater than necessary if any
increase in fan rpm is likely in the future.
P.O. Box 410 • Schofield, WI 54476-0410 • Phone (715) 359-6171 • greenheck.com
Fan Fundamentals Rev 2 June 2005
Copyright © 2005 Greenheck Fan Corp.
Fan Laws