14
The overload is wired in series with the common motor
terminal. The overload senses both major amperage and
compressor temperature. High motor temperature or
amperage heats the disc causing it to open and break the
circuit to the common motor terminal.
COMPONENTS:
OPERATION & TESTING
WARNING
DISCONNECT ELECTRICAL POWER TO
UNIT BEFORE SERVICING OR TESTING
COMPRESSORS
Compressors are single phase, 115 or 230/208 volt,
depending on the model unit. All compressor motors are
permanent split capacitor type using only a running capacitor
across the start and run terminal.
All compressors are internally spring mounted and externally
mounted on rubber isolators.
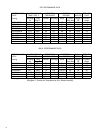
WINDING TEST
Remove compressor terminal box cover and disconnect wires
from terminals. Using an ohmmeter, check continuity across
the following: (See Figure 1)
1. Terminal "C" and "S" - no continuity - open winding -
replace compressor.
2. Terminal "C" and "R" - no continuity - open winding -
replace compressor.
3. Terminal "R" and "S" - no continuity - open winding -
replace compressor.
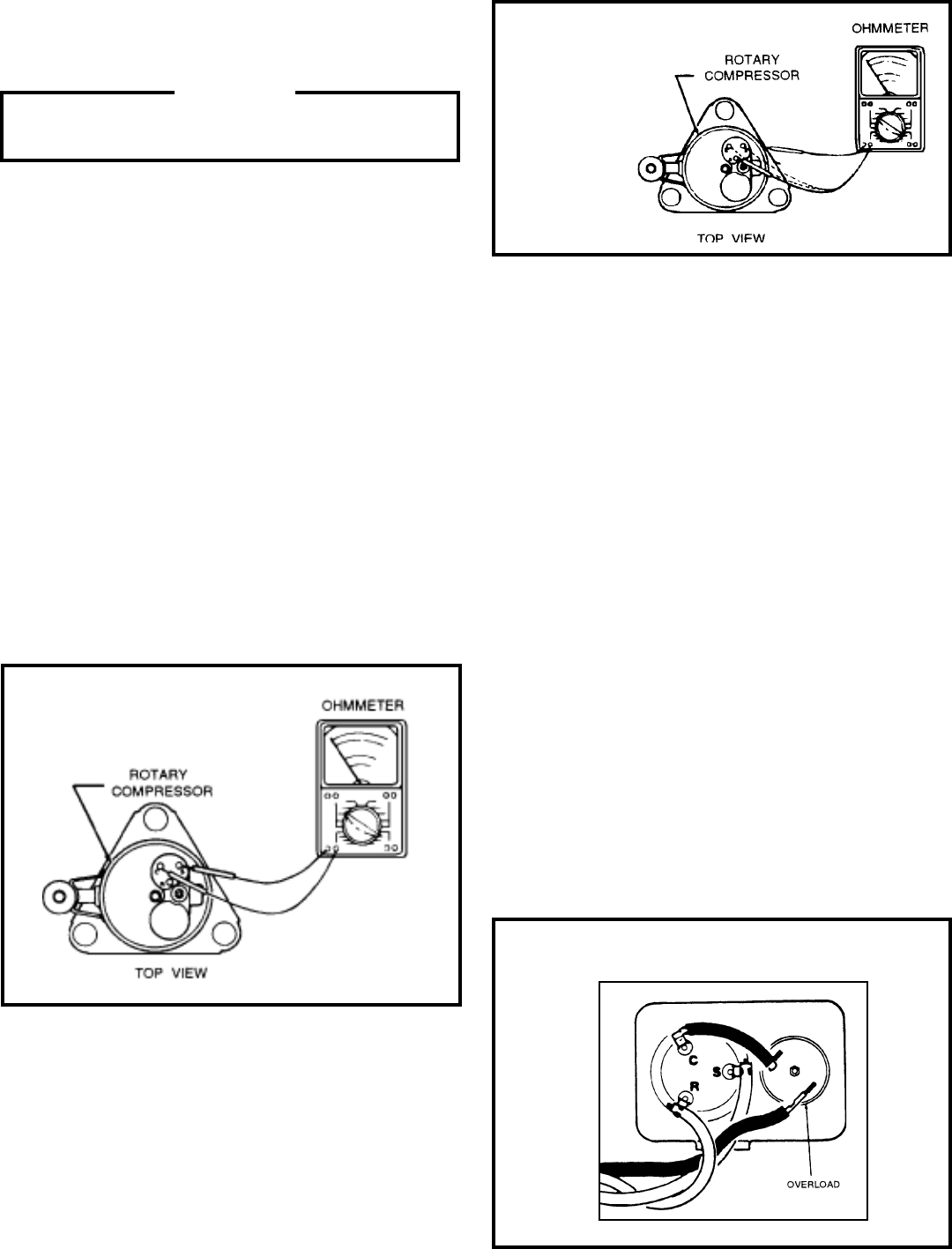
GROUND TEST
Use an ohmmeter set on its highest scale. Touch one lead to
the compressor body (clean point of contact as a good con-
nection is a must) and the other probe in turn to each com-
pressor terminal (see Figure 2.) If a reading is obtained, the
compressor is grounded and must be replaced.
CHECKING COMPRESSOR EFFICIENCY
The reason for compressor inefficiency is normally due to broken
or damaged suction and/or discharge valves, reducing the ability
of the compressor to pump refrigerant gas.
This condition can be checked as follows:
1. Install a piercing valve on the suction and discharge or
liquid process tube.
2. Attach gauges to the high and low sides of the system.
3. Start the system and run a “cooling or heating
performance test.”
If test shows:
A. Below normal high side pressure
B. Above normal low side pressure
C. Low temperature difference across coil
The compressor valves are faulty - replace the
compressor.
THERMAL OVERLOAD (External)
Some compressors are equipped with an external overload
which is located in the compressor terminal box adjacent to
the compressor body (See Figure 3.)
Figure 1
Figure 3- External Overload
Figure 2
Typical Ground Test