Chart Environmental Chambers Features
Features
❏ Temperature Control System:
Heating is accomplished with resistive electric elements, while cooling is accomplished
by blowing liquid nitrogen into the chamber. The liquid nitrogen is vaporized through
nozzles and the cold vapor is circulated over the products in the chamber so that liquid
nitrogen does not touch the product under test. Electric heaters are carefully selected and
arranged to provide extremely rapid rates of temperature change without exceeding safe
design limits of heat elements. The heaters and nitrogen nozzles are located in the air
conditioning plenum.
CAUTION: Although the chamber is designed to use very small amounts of liquid
nitrogen, the resulting nitrogen gas is vented out of the chamber. It is
important to monitor the oxygen levels in the working environment around
the chamber to ensure safe operating conditions.
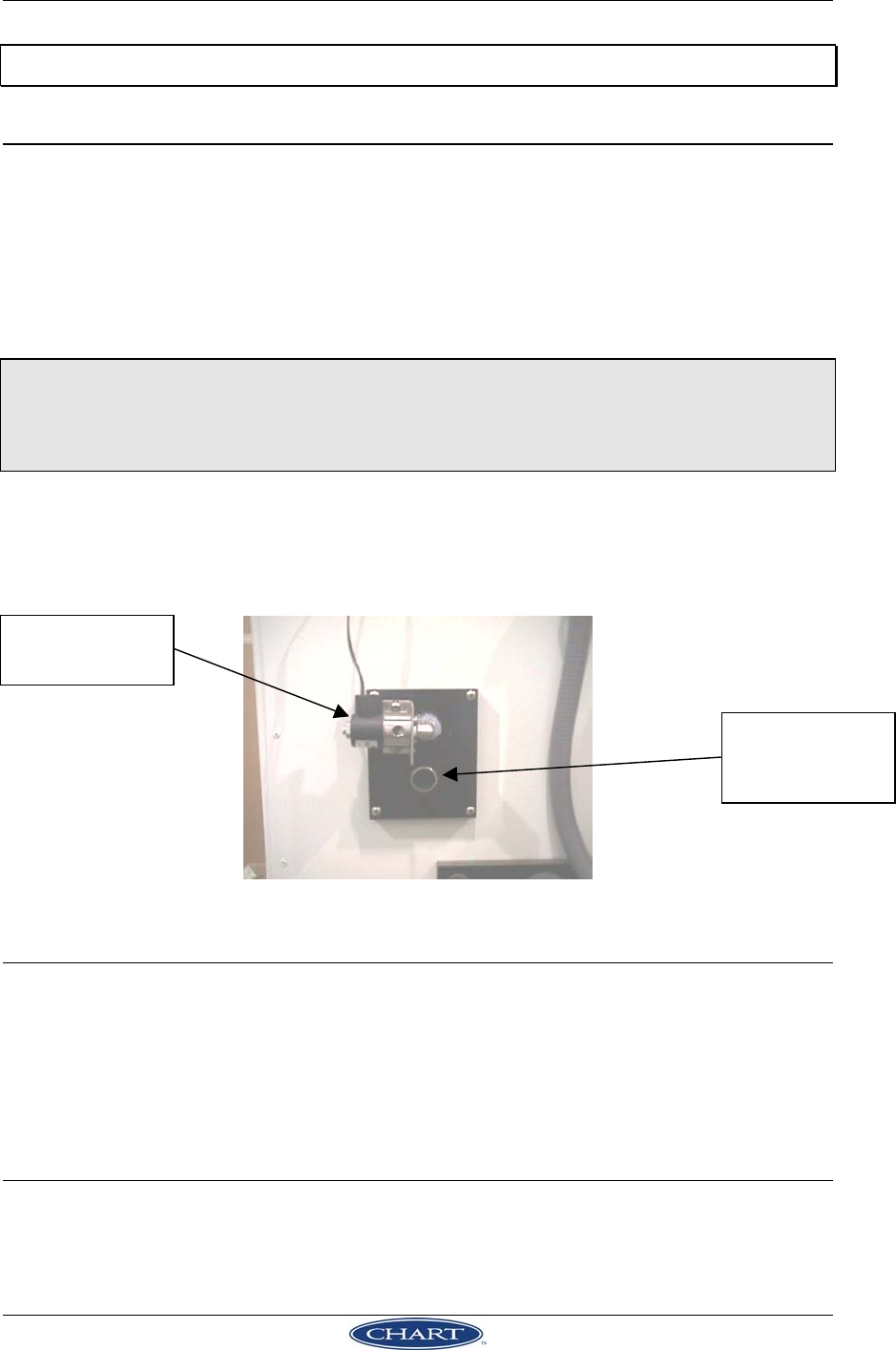
The liquid nitrogen control is done by a solenoid valve. The solenoid valve is chosen for
its compact size and high reliability. The temperature controller tells the solenoid valve
when to open based on the temperature inside the chamber.
Cooling solenoid
valve.
Nitrogen gas
exhaust.
❏ Air Circulation Blower:
The chamber is equipped with a non-corrosive blower wheel, which provides air
circulation to distribute temperature controlled air and minimize thermal enclosure
temperature gradients. Baffles provide output air openings to direct the air flow out of the
duct and into the workspace of the chamber. The blower is located in the air
conditioning plenum. The blower draws air flow across the heater and nitrogen nozzle
and out into the workspace of the chamber.
❑ Instruments:
Temperature is controlled by a Watlow Series 96 temperature controller. The input to the
temperature controller is a type T thermocouple. The control thermocouple is mounted in
5


















