Page 6 16943-5-0806
Water vapor is a by-product of gas combustion. An unvented room
heater produces approximately one (1) ounce (30ml) of water for
every 1,000 Btu (.3KW's) of gas input per hour.
Unvented room heaters must be used as supplemental heat (a
room) rather than a primary heat source (an entire house). In most
supplemental heat applications, the water vapor does not create a
problem. In most applications, the water vapor enhances the low
humidity atmosphere experienced during cold weather.
The following steps will help insure that water vapor does not
become a problem.
1. Be sure the heater is sized properly for the application, including
ample combustion air and circulation air.
2. If high humidity is experienced, a dehumidifier may be used to
help lower the water vapor content of the air.
3. Do not use an unvented room heater as the primary heat source
(an entire house).
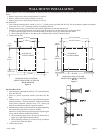
This heater shall not be installed in a confined space or unusually
tight construction unless provisions are provided for adequate
combustion and ventilation air.
The National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 defines a confined space
as a space whose volume is less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per
hour (4.8m
3
per kw) of the aggregate input rating of all appliances
installed in that space and an unconfined space as a space whose
volume is not less than 50 cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour (4.8m
3
per kw) of the aggregate input rating of all appliances installed in
that space. Rooms communicating directly with the space in which
the appliances are installed, through openings not furnished with
doors, are considered a part of the unconfined space.
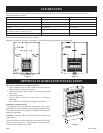
The following example is for determining the volume of a typical
area in which the BF-20 may be located and for determining if this
area fits the definition of an unconfined space.
The input of the BF-20 is 20,000 Btu per hour. Based on the 50
cubic feet per 1,000 Btu per hour formula, the minimum area that
is an unconfined space for installation of the BF-20 is 1,000 cubic
feet, 50 cubic feet x 20 = 1,000 cubic feet. To determine the cubic
feet of the area in which the BF-20 is to be installed, measure the
length, width and height of the area. Example: The area measures
16 feet in length, 8 feet in width and 8 feet in height, the area is
1,024 cubic feet. The BF-20 can be installed in this unconfined
space with no requirement to provide additional combustion and
ventilation air.
Warning: If the area in which the heater may be operated is smaller
than that defined as an unconfined space or if the building is of
unusually tight construction, provide adequate combustion and
ventilation air by one of the methods described in the National Fuel
Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1, Section 5.3 or applicable local codes.
Unusually Tight Construction
The air that leaks around doors and windows may provide enough
fresh air for combustion and ventilation. However, in buildings
of unusually tight construction, you must provide additional fresh
air.
Unusually tight construction is defined as construction where:
a. Walls and ceilings exposed to the outside atmosphere have
a continuous water vapor retarder with a rating of one perm
or less with openings gasketed or sealed, and
b. Weatherstripping has been added on openable windows and
doors, and
c. Caulking or sealants are applied to areas such as joints
around window and door frames, between sole plates and
floors, between wall-ceiling joints, between wall panels, at
penetrations for plumbing, electrical, and gas lines, and at
other openings.
If the heater is installed in a building of unusually tight construction,
adequate air for combustion, ventilation and dilution of flue gases
shall be provided in accordance with ANSI Z223.1/NFPA54.
WATER VAPOR: A BY-PRODUCT OF UNVENTED ROOM HEATERS
PROVISIONS FOR ADEQUATE COMBUSTION & VENTILATION AIR