If the actual Btu/Hr used is less than the max-
imum Btu/Hr the space can support, the space
is an unconfined space. You will need no addi-
tional fresh air ventilation.
VENTILATION AIR
Ventilation Air From Inside Building
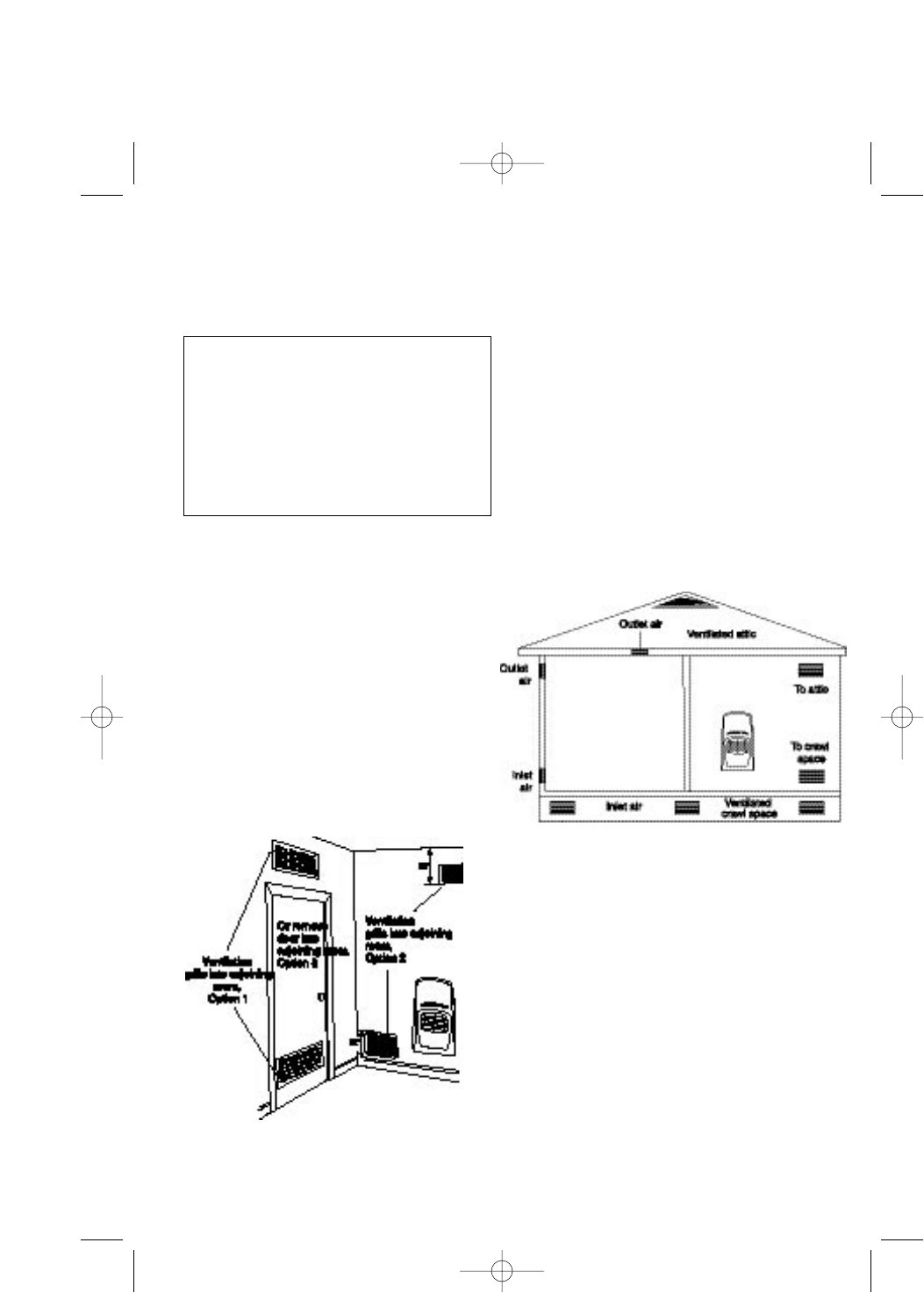
This fresh air would come from an adjoining
unconfined space.
When ventilating to an adjoining unconfined
space, you must provide two permanent open-
ings: one within 12” of the ceiling and one
within 12” of the floor on the wall connecting
the two spaces (see options 1 and 2, figure
??). Follow the National Fuel gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFA 54, section air for combustion
and ventilation for required size of ventilation
grills or ducts.
Ventilation Air From Outdoors
Provide extra fresh air by using ventilation grilles
or ducts. You must provide two permanent open-
ings: one within 12”of the ceiling and one within
12” of the floor. Connect these items directly to the
outdoors. These spaces include attics and crawl
spaces. Follow the National Fuel gas Code, ANSI
Z223.1/NFA 54, section air for combustion and
ventilation for required size of ventilation grills or
ducts.
IMPORTANT: Do not provide openings for inlet
or outlet air into attic has a thermostat-con-
trolled power vent. Heated air entering the
attic will activate the power vent.
6
WARNING: if the area in which the heater
may be operated is smaller than that defined
as an unconfined space or if the building is of
unusually tight construction, provide adequate
combustion and ventilation air by one of the
methods described in the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54 section 5.3 or
applicable local codes.
Fig.2 Ventilation Air from Inside Building
Fig.3 Ventilation Air From Outdoors
WIR 2 26-06-2003 18:21 Pagina 6


















