Configuring Modular Quality of Service Congestion Management on Cisco IOS XR Software
Information About Configuring QoS Congestion Management on Cisco IOS XR Software
QC-34
Cisco IOS XR Modular Quality of Service Configuration Guide
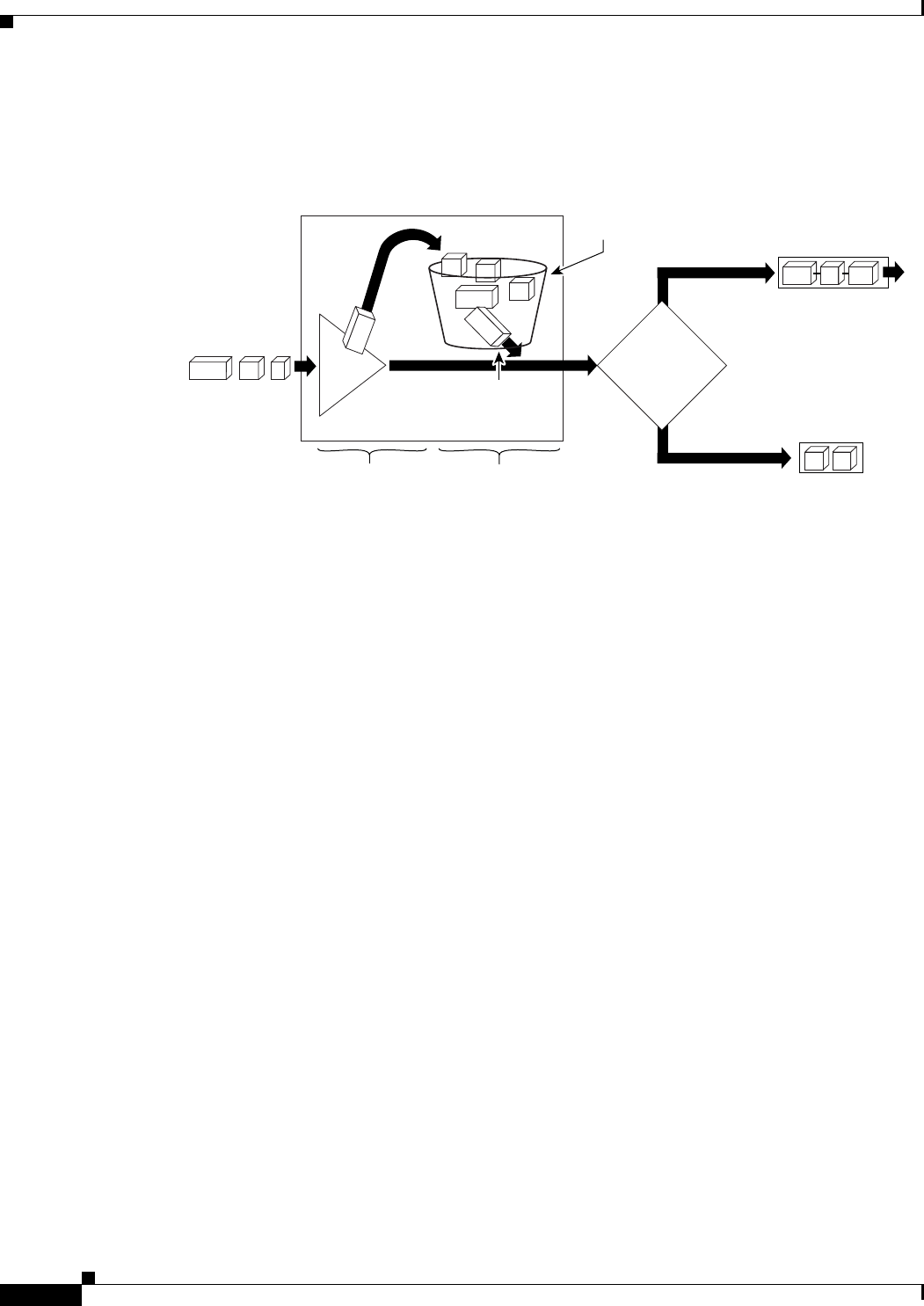
Figure 2 illustrates how a traffic shaping mechanism regulates traffic flow.
Figure 2 How a Traffic Shaping Mechanism Regulates Traffic
Packets matching the specified criteria are placed in the token bucket. The maximum size of the token
bucket is the confirm burst (Bc) size plus the Be size. The token bucket is filled at a constant rate of Bc
worth of tokens at every Tc. This is the configured traffic shaping rate.
If the traffic shaping mechanism is active (that is, packets exceeding the configured traffic shaping rate
already exist in a transmission queue) at every Tc, the traffic shaper checks to see if the transmission
queue contains enough packets to send (that is, up to either Bc [or Bc plus Be] worth of traffic).
If the traffic shaper is not active (that is, there are no packets exceeding the configured traffic shaping
rate in the transmission queue), the traffic shaper checks the number of tokens in the token bucket. One
of the following occurs:
• If there are enough tokens in the token bucket, the packet is sent (transmitted).
• If there are not enough tokens in the token bucket, the packet is placed in a shaping queue for
transmission at a later time.
Traffic Policing
In general, traffic policing allows you to control the maximum rate of traffic sent or received on an
interface, and to partition a network into multiple priority levels or class of service (CoS).
Traffic policing manages the maximum rate of traffic through a token bucket algorithm. The token bucket
algorithm can use the user-configured values to determine the maximum rate of traffic allowed on an
interface at a given moment in time. The token bucket algorithm is affected by all traffic entering or
leaving (depending on where the traffic policy with traffic policing is configured) and is useful in
managing network bandwidth in cases in which several large packets are sent in the same traffic stream.
Traffic entering the interface with traffic policing configured is placed into one of these categories.
Within these three categories, users can decide packet treatments. For instance, packets that conform can
be configured to be sent, packets that exceed can be configured to be sent with a decreased priority, and
packets that violate can be configured to be dropped.
Classify
Incoming packets
"Token bucket"
shaping
Packet classification
criteria applied
(e.g., via the MQC)
117493
Match
Token bucket
Ye s
No
Configured
traffic shaping rate
Enough
tokens in
the token
bucket?
Outgoing packets
placed in shaping queue
(transmitted later)
Outgoing packets
transmitted
