15-15
Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide
OL-12172-01
Chapter 15 Firewall Mode Overview
Transparent Mode Overview
If the destination MAC address is not in the security appliance table, the security appliance attempts
to discover the MAC address by sending an ARP request and a ping. The first packet is dropped.
5. The web server responds to the request; because the session is already established, the packet
bypasses the many lookups associated with a new connection.
6. The security appliance forwards the packet to the outside user.
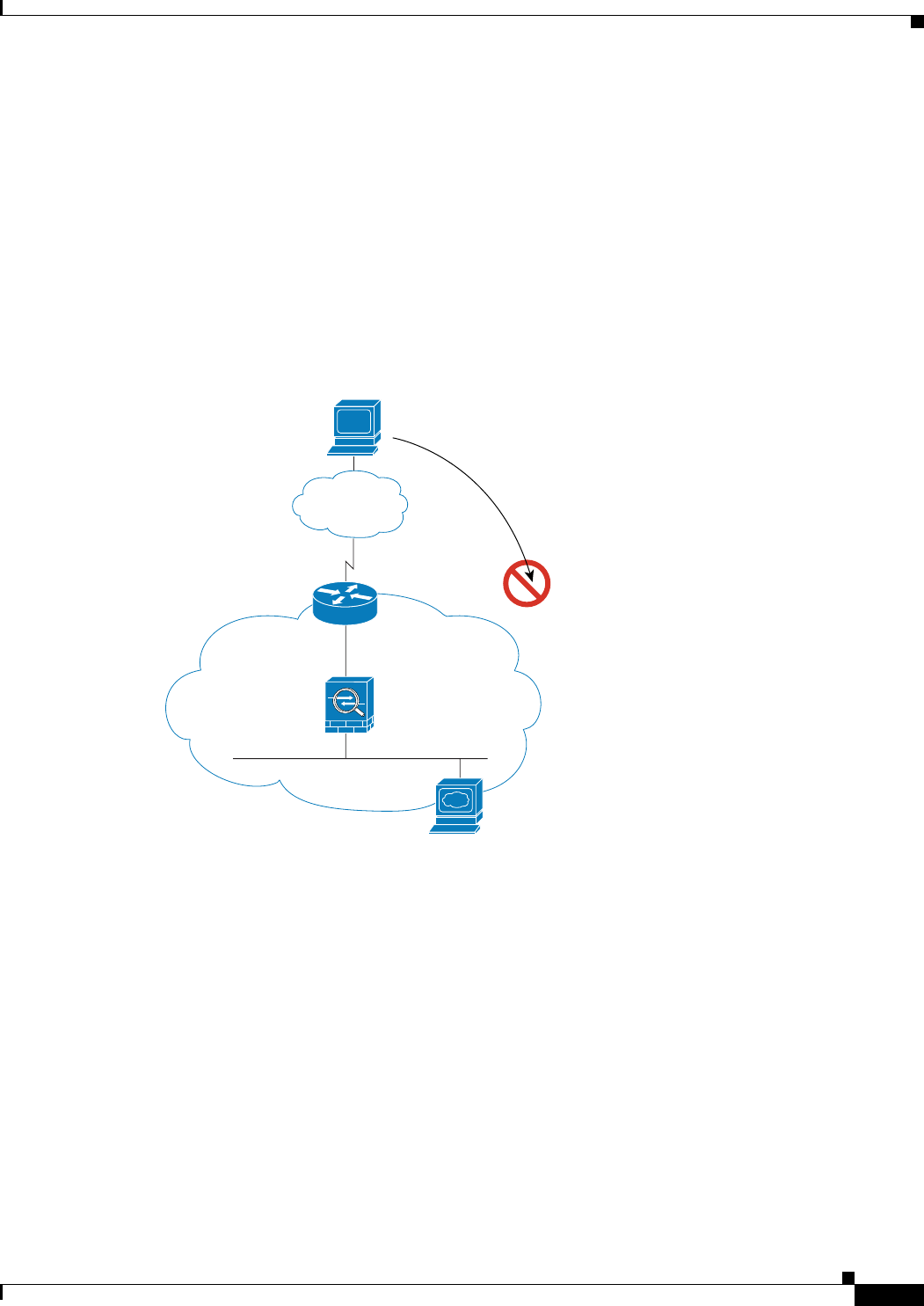
An Outside User Attempts to Access an Inside Host
Figure 15-11 shows an outside user attempting to access a host on the inside network.
Figure 15-11 Outside to Inside
The following steps describe how data moves through the security appliance (see Figure 15-11):
1. A user on the outside network attempts to reach an inside host.
2. The security appliance receives the packet and adds the source MAC address to the MAC address
table, if required. Because it is a new session, it verifies if the packet is allowed according to the
terms of the security policy (access lists, filters, AAA).
For multiple context mode, the security appliance first classifies the packet according to a unique
interface.
3. The packet is denied, and the security appliance drops the packet.
4. If the outside user is attempting to attack the inside network, the security appliance employs many
technologies to determine if a packet is valid for an already established session.
Management IP
209.165.201.6
Host
209.165.201.2
Host
209.165.201.3
Internet
92410


















