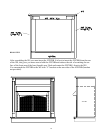
3. Add the BTU/Hr of all fuel burning appliances in the space.
Vent-Free Heater _________________________BTU/Hr.
Gas Water Heater* _________________________BTU/Hr.
Gas Furnace _________________________BTU/Hr.
Vented Gas Heater _________________________BTU/Hr.
Gas Fireplace Logs _________________________BTU/Hr.
Other Gas Appliance* +_________________________BTU/Hr.
Total = _________________________BTU/Hr.
Example: Gas water heater 40000 BTU/Hr.
Vent-free heater + 18000 BTU/Hr.
Total = 58000 BTU/Hr.
* Does not include direct-vent gas appliances. Direct-vent draws combustion
air from the outdoors and vents to the outdoors.
4. Compare the maximum BTU/Hr the space can support with the actual amount
of BTU/Hr used.
_____________BTU/Hr (maximum the space can support)
_____________BTU/Hr (actual amount of BTU/Hr used)
Example: 51200 BTU/Hr (maximum the space can support)
58000 BTU/Hr (actual amount of BTU/Hr used)
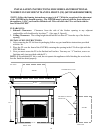
The space in the above example is a confined space because the actual BTU/Hr used is more than the
maximum BTU/Hr the space can support. Additional fresh air must be provided. The following
options are available.
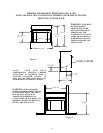
A. Rework worksheet, adding the space of an adjoining room. If the extra space provides an
unconfined space, remove door to adjoining room or add ventilation grills between rooms. See
“Ventilation Air From Inside Building”, page 15.
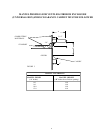
B. Vent room directly to the outdoors. See “Ventilation Air From Outdoors” page 16.
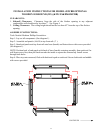
C. Install a lower BTU/Hr heater, if lower BTU/Hr size makes room unconfined.
If the actual BTU/Hr used is less than the maximum BTU/Hr the space can support, the space is
unconfined. You will need no additional fresh air ventilation.
WARNING
YOU MUST PROVIDE ADDITIONAL VENTILATION AIR IN A CONFINED SPACE
14