28
SELECTION PROCEDURE (WITH 580J*07A EXAMPLE)
1
I. Determine cooling and heating loads.
Given:
Mixed air dry bulb 80_F(27_C)
Mixed air wet bulb 67_F(19_C)
Ambient dry bulb 95_F(35_C)
TC
Load
72.0 MBH
SHC
Load
54.0 MBH
Vertical supply air 2100 CFM
Heating load 85.0 MBH
External static pressure 0.67 in. wg
Electrical characteristics 230--3--60
II. Make an initial guess at cooling tons.
Refrig. tons = TC
Load
/ 12 MBH per ton
Refrig. tons = 72.0 / 12 = 6.0 tons
In this case, start by looking at the 580J*07.
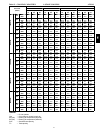
III. Look up the rooftop’s TC and SHC.
Table 15 shows that, at the application’s supply air
CFM, mixed air and ambient temperatures, the
580J*07A supplies:
TC = 73.7 MBH
2
SHC = 54.4 MBH
2
IV. Calculate the building latent heat load.
LC
Load
=TC
Load
-- S H C
Load
LC
Load
= 72.0 MBH -- 54.0 MBH = 18.0 MBH
V. Calculate RTU latent heat capacity.
LC = TC -- SHC
LC = 73.7 MBH -- 54.4 MBH = 19.3 MBH
VI. Compare RTU capacities to loads.
3
Compare the rooftop’s SHC and LC to the
building’s sensible and latent heat loads.
VII. Select factory options (FIOP)
Local code requires an economizer for any unit with
TC greater than 65.0 MBH.
VIII.Calculate the total static pressure.
External static pressure 0.67 in. wg
Sum of FIOP / Accessory static +0.13 in.
wg
Total Static Pressure 0.80 in. wg
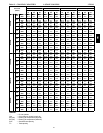
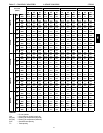
IX. Look up the indoor fan RPM & BHP.
Table 36 shows, at 2100 CFM & ESP= 0.8,
RPM = 1358 & BHP = 1.52
X. Convert BHP (Step VIII) into fan motor heat.
Fan motor heat = 2.546* BHP/Motor Eff.
4
Fan motor heat = 4.9 MBH
XI. Calculate RTU heating capacity.
Building heating load 85.0 MBH
Fan motor heat --4.9
MBH
Required heating capacity 80.1 MBH
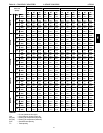
XII. Select a gas heater.
Table 4 shows the heating capacities of the
580JE07A = 93.0 MBH. Select the 580JE07A
XIII.Determine electrical requirements.
Table 56 shows the MCA and MOCP of a 580J*07A
(without convenience outlet) as:
MCA = 30.5 amps & MOCP = 45.0 amps
Min. disconnect size: FLA = 30 & LRA = 157.
LEGEND
BHP — Brake horsepower
FLA — Full load amps
LC — Latent capacity
LRA — Lock rotor amp
MBH — (1,000) BTUH
MCA — Min. circuit ampacity
MOCP — Max. over---current protection
RPM — Revolutions per minute
RTU — Rooftop unit
SHC — Sensible heat capacity
TC — Total capacity
NOTES:
1. Selection software by Bryant saves time by performing
many of the steps above. Contact your Br yant sales
representative for assistance.
2. Unit ratings are gross capacit ies and do not include the
effect of evaporator fan motor heat. See Step X. for de-
termining amount of evaporator fan motor heat to sub-
tract from total and sensible capacities to obtain net
coo ling and net sensibl e capacities.
3. Selecting a unit with a SHC slightly lower than the
SHC
Load
is often better than oversizing. Slightly lower
SHC’s will help control indoor humidity, and prevent
temperature swings.
4. Indoor fan motor efficiency is available in Table 45. Use
the decimal form in the equation, eg. 80% = .8.
580J