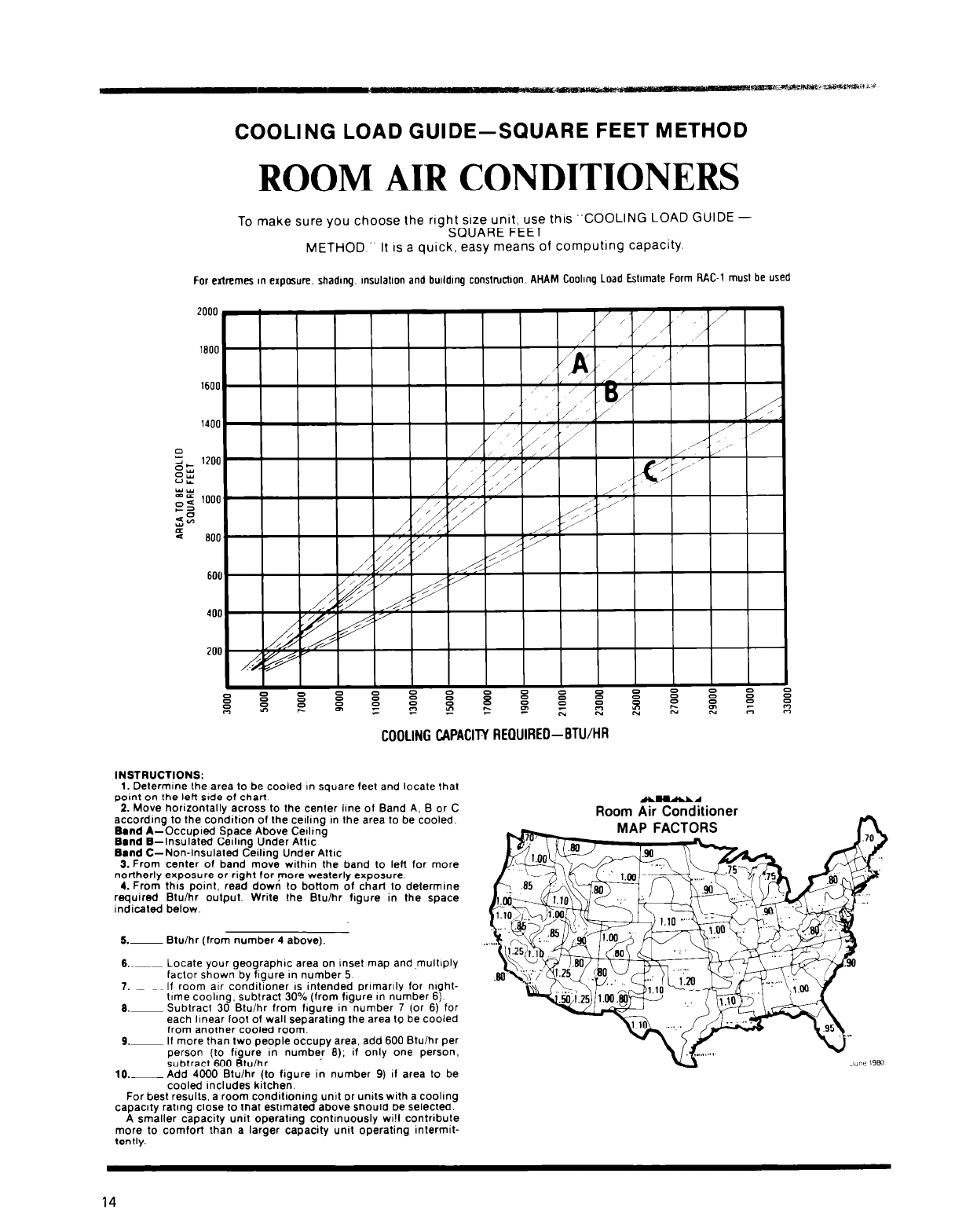
COOLING LOAD GUIDE-SQUARE FEET METHOD
ROOM AIR CONDITIONERS
To make sure you choose the rtght stze unit, use thts “COOLING LOAD GUIDE -
SQUARE FEET
METHOD ” It IS a quick. easy means of computing capacity.
For extremes tn espmure shadtng msulalton and butldtng construction. AHAM Coohng Load Esltmale Form FIAC-1 must be used
1600
6Ot
COOLING CAPACITY REQUIREO-BTU/HR
INSTRUCTIONS:
1. Determine Ihe area lo be cooled In square feet and locale that
point on the left srde of chart
2. Move horizontally across to the center lrne of Band A, 0 or C
according to the condition of the cethng in the area to be cooled.
Band A-Occupied Space Above Ceding
Bmnd B-Insulated Ceiling Under Athc
Band C-Non-Insulated Ceiling Under Attrc
3. From center of band move within the band to left for more
northerly exposure or right for more westerly exposure.
4. From thus point, read down to bonom of chart to determine
required Btu/hr output. Write the Btulhr figure in the space
indicated below.
5.- Btulhr (from number 4 above).
6.--- Locate your geographrc area on Inset map and multlply
factor shown by figure rn number 5
?.~-_ If room air conditioner IS intended prlmarlly for nrghl-
time coohng, subtract 30% (from figure In number 6)
6.p
Subtract 30 Btuihr from ftgure in number 7 (or 6) for
each linear foot of wall seoaratino the area lo be cooled
from another cooled room. -
9.-
If more than two people occupy area. add 600 Btuihr per
person (to figure rn number 8); if only one person,
subtracl 600 Btu/hr.
lo.-
Add 4000 Btu/hr (to figure in number 9) if area to be
cooled tncludes krtchen.
For best results, a room condittonmg unit or umts with a cooling
capacity rahng close to that estimatedabove should be selected:
A smaller capacity unit operatmg conhnuously wi!l contribute
more to comfort than a larger capacity unit operating inlermit-
tently.
Room Air Conditioner
--
MAP FACTORS
n
14


















