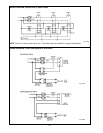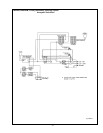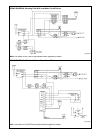
Fig. #8964
PILOT BURNER FLAME (STANDING PILOT UNITS)
INSPECTION PROCEDURES
To be performed the first and third month after initial
start up and then on an annual basis. If problems are
found, refer to Troubleshooting Guide for additional direc-
tions.
1. Remove top of boiler and inspect heat exchanger
for soot and examine venting system.
2. Remove rear header and inspect for scale depos-
its.
*3. Inspect pilot and main burner flame and firing rate.
*4. Inspect and operate all controls and gas valve.
*5. Visually inspect system for water leaks.
*6. Inspect oil pump motor and bearing assembly, if oil
cups are provided.
7. Check flow switch paddle.
8. Clean room air intake openings to ensure adequate
flow of combustion and ventilation air.
9. Keep boiler area clear and free from combustible
materials, gasoline, and other flammable vapors
and liquids.
*Should be checked monthly. (Takes approximately 15
minutes).
SAFE SHUT-DOWN TESTS
LIMIT ACTION
With the burner operating, lower the high limit
setting to simulate an overheated boiler. Normal shut-
down should occur. Restore the normal limit setting,
and the burner should restart.
FLAME FAILURE
With burner operating, close the manual fuel valves
to simulate a flame failure. System should lock out after
safety switch timing (15 seconds). After the safety
switch has cooled, open the manual valves (relight
standing pilots) and reset the safety switch; the burner
should restart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURES
BURNERS
Clean main burners and air louvers of dust, lint and
debris. Keep boiler area clear and free from combustibles
and flammable liquids. Do not obstruct the flow of
combustion and ventilation air. Make visual check of
burner and pilot flame. Yellow flame indicates clogging of
air openings. Lifting or blowing flame indicates high gas
pressure. Low flame indicates low gas pressure.
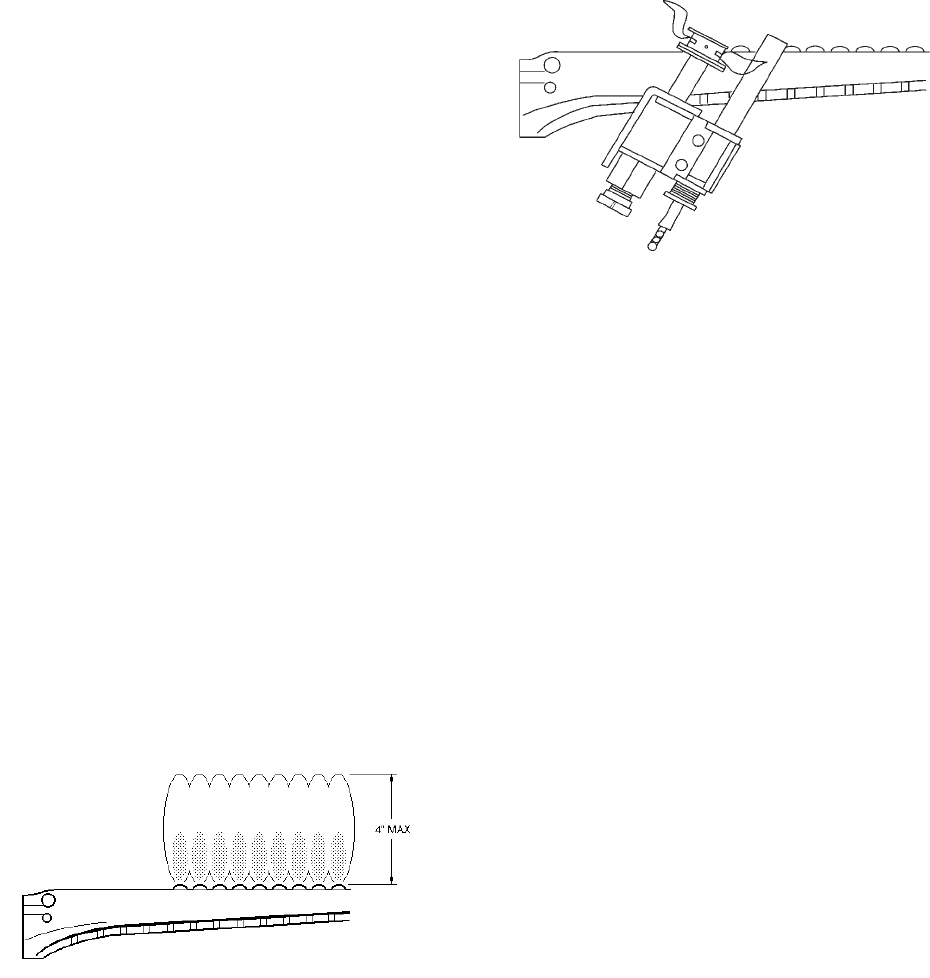
Fig. #8144
MAIN BURNER FLAME
NOTE: Modulating burner flame varies in height from
approximately 1/4" at low fire to approximately 4" in
high fire.
28