PI-MAX2 DIF Camera
May 26, 2004 6 of 8 Princeton Instruments
E:\Ma nuals\Syst ems\PI-MAX\PI-M AX2 DIF Ca mera.doc
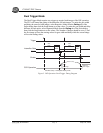
4. Now the PTG needs to be programmed to match the experiment. In the
Setup
menu, select Pulser and click on Pulser Setup (or click the
Pulser Setup
button in the Custom Toolbar).
a. In the Pulser dialog, select the
Trigger
tab. The PTG can be triggered by an
external trigger signal such as a TTL (typical settings for a TTL trigger might
be: 1.7 V, positive edge, DC, 50 Ohm) or a photodiode (typical settings for a
photodiode might be: 8.0 V, positive edge, DC, high Z), or the PTG can use
its own internal clock to trigger the experiment. Select the appropriate one
for your experiment. In either case, the trigger frequency should be slow
enough so that the period between triggers is longer than the Gate Delay +
Gate Width + Phosphor Decay time.
b. Now select the
Gating
tab. If the experiment can use the same gate width
and delay for both frames, then select Repetitive, and click on the
Setup
button to set the appropriate gate width and delay. If the experiment requires
different gate widths or delays for each frame, then select Sequential and
click on the
Setup
button to set the appropriate gate widths and delays. The
number of images should be set to 2, the gate width and delay for the first
frame should be set as the starting values, and the width and delay for the
second frame should be set as the ending values.
c. At the bottom of the Pulser Setup dialog, click
OK
to download the gating
sequence to the PTG.
5. The CCD parameters need to be set to the appropriate values for DIF operation.
Select Experiment Setup from the
Acquisition
menu.
a. On the
Timing
tab, select Dual Trig. Mode.
b. On the
Main
tab, verify that the Number of Images is 2 and the Intensifier is
in Gate Mode.
c. When the experiment is ready, click the
Acquire
button to start the image
acquisition.
Tips and Tricks
Experiments using the DIF feature of the PI-MAX2 can be complex, and timing of the
events is usually rather exacting. Here are several points to consider that may make the
experiment setup or troubleshooting much smoother and easier.
• The most important piece of equipment in a DIF experiment is an oscilloscope.
The PI-MAX2 has a Gate Monitor signal on the back of the camera head which
is very useful for seeing when the two image exposures occur during the course
of the experiment. The use of the Gate Monitor and an oscilloscope is discussed
in more detail in Chapter 11: Tips and Tricks.
Note: If you have an older version of the PI-MAX/PI-MAX2 system manual,
refer to Chapter 10.
• The short time between the two images in DIF requires an intensifier with a fast
phosphor. P46 phosphor as a decay time of ~ 2 µs, that means it takes 2 µs for