[ IX Troubleshooting ]
- 235 -
HWE09120 GB
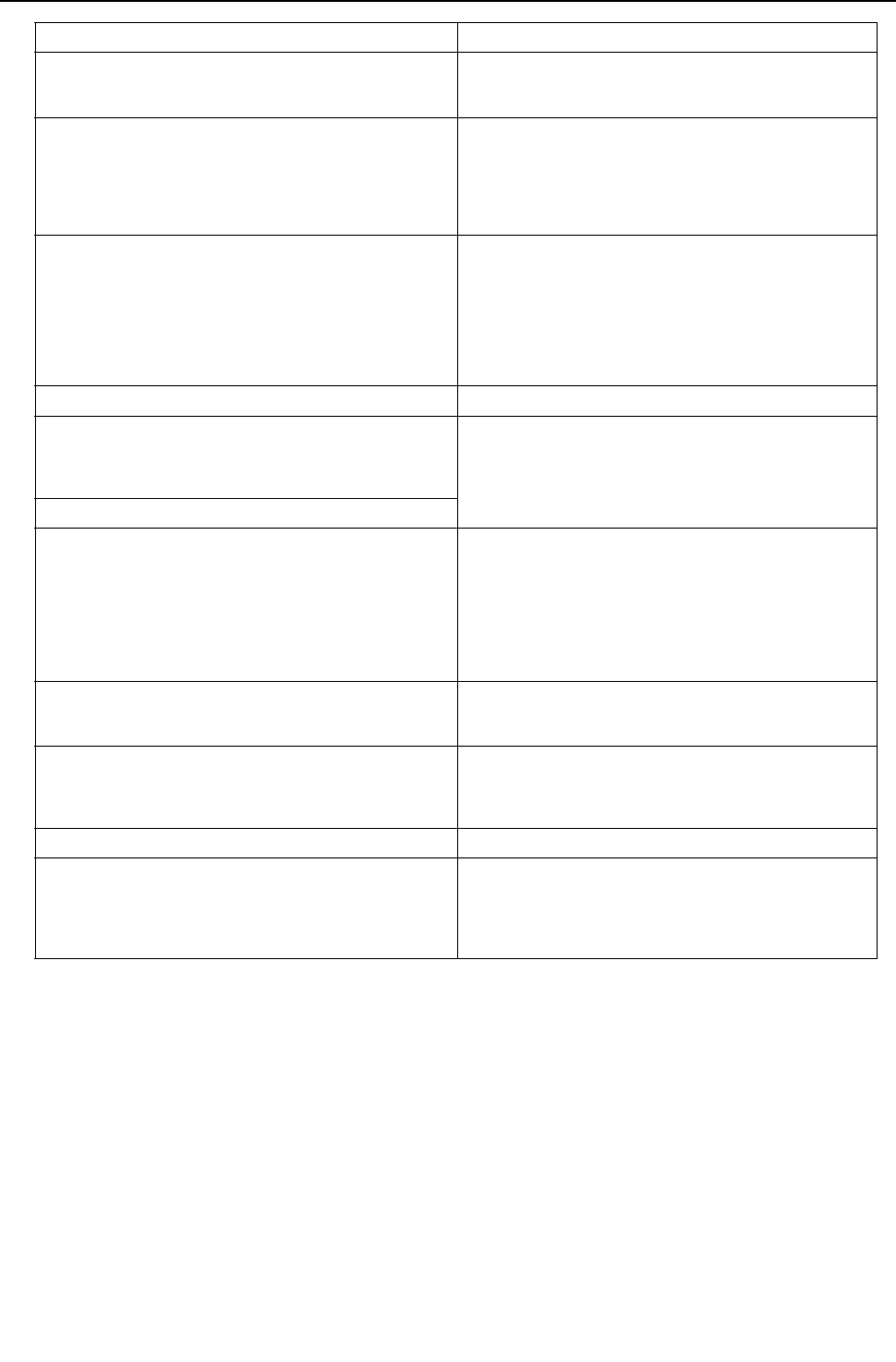
Cause Check method and remedy
2. Indoor unit LEV malfunction
Insufficient refrigerant flows due to LEV malfunction
(not enough opening).
Refer to the page of LEV troubleshooting ([4] -5-
).(page 245)
3. Temperature reading error on the indoor unit piping
temperature sensor
If the temperature reading on the sensor is higher
than the actual temperature, it makes the subcool
seem smaller than it is, and the LEV opening de-
creases too much.
Check the thermistor.
4 RPM error of the outdoor unit FAN Refer to the page on outdoor unit fan ([4] -4-
).(page 243)
Motor failure or board failure, or airflow rate de-
crease, pressure drop due to clogging of the heat
exchanger leading to high discharge temperature
The fan is not properly controlled as the tempera-
ture cannot be precisely detected with the piping
sensor.
5. Insulation failure of the refrigerant piping
6. Long piping length
Excessively long piping on the high pressure side
causes pressure loss leading to increase in the high
pressure.
Confirm that the characteristic of capacity drop due
to piping length.
-> Change the pipe
7. Piping size is not proper (thin)
8. Clogging by foreign object Check the temperature difference between the up-
stream and the downstream of the pipe section that
is blocked. Since blockage in the extended section
is difficult to locate, operate the unit in the cooling
cycle, and follow the same procedures that are
used to locate the blockage of pipe during cooling
operation.
->Remove the blockage in the pipe.
9. The indoor unit inlet temperature is excessively
high.(exceeding 28°C [82°F])
Check the inlet air temperature and for short cy-
cling. Change the environment where the indoor
unit is used.
10. Insufficient refrigerant amount
Protection works and compressor frequency does
not rise due to low discharge temperature
Refrigerant recovery operation is likely to start.
Refer to 2 - 1. (Compressor frequency does not rise
sufficiently.)(page 234)
Refer to the page on refrigerant amount
adjustment.(page 125)
11. Compressor failure (same as in case of cooling) Check the discharge temperature.
12. LEV2 actuation failure
A drop in the low pressure that is caused either by a
blockage of liquid pipe or by a pressure loss and the
resultant slowing of refrigerant flow causes a tenden-
cy for the discharge temperature to rise.
Refer to the page on troubleshooting the LEV ([4] -
5-).(page 245)