Restricted Refrigerant System
Troubleshooting a restricted refrigerant system can be
difcult. The following procedures are the more common
problems and solutions to these problems. There are two
types of refrigerant restrictions: Partial restrictions and
complete restrictions.
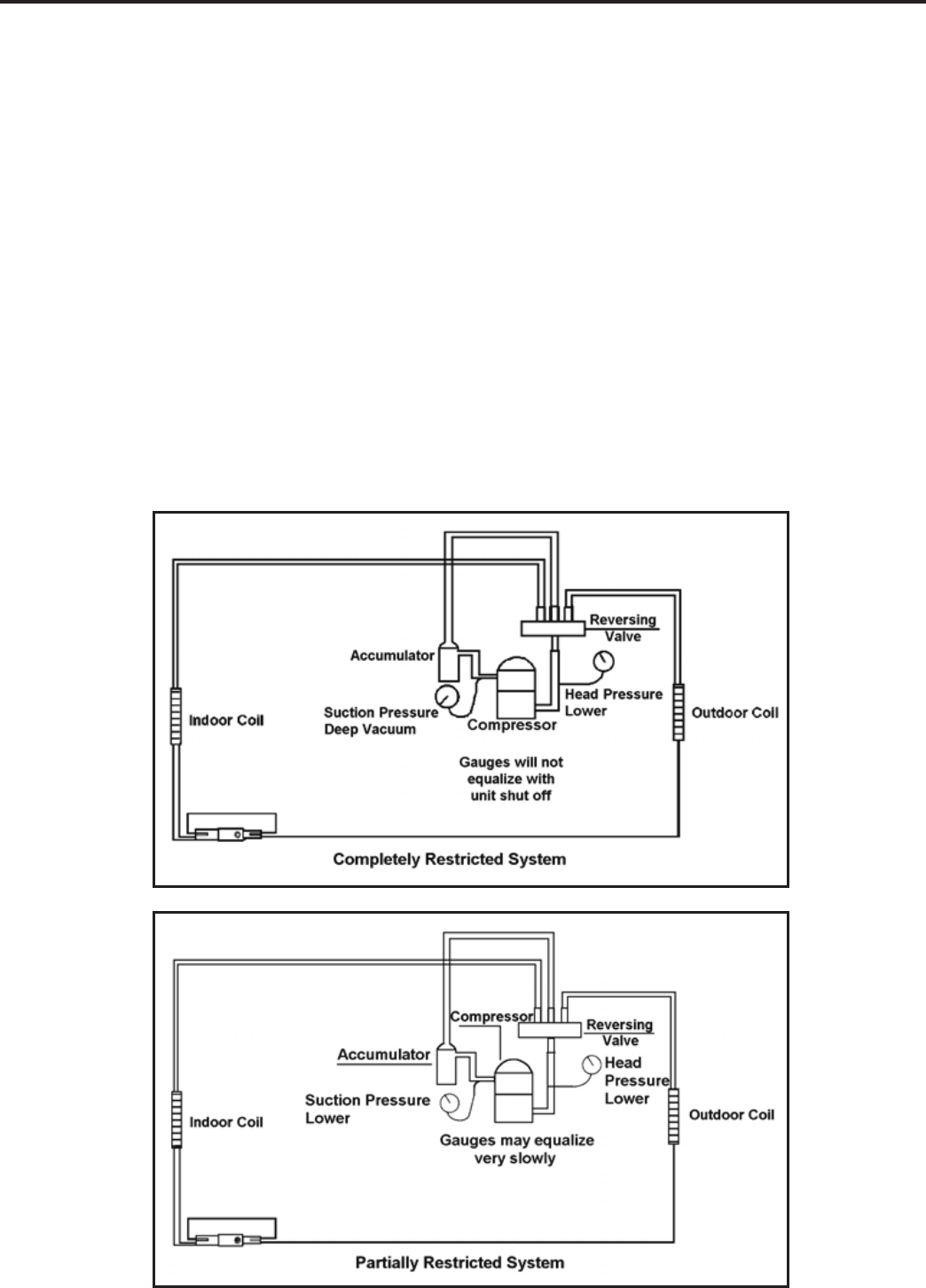
A partial restriction allows some of the refrigerant to
circulate through the system.
With a complete restriction there is no circulation of
refrigerant in the system.
Restricted refrigerant systems display the same symptoms
as a “low-charge condition.”
When the unit is shut off, the gauges may equalize very
slowly.
Gauges connected to a completely restricted system will
run in a deep vacuum. When the unit is shut off, the gauges
will not equalize at all.
A quick check for either condition begins at the evaporator.
With a partial restriction, there may be gurgling sounds
at the metering device entrance to the evaporator. The
evaporator in a partial restriction could be partially frosted
or have an ice ball close to the entrance of the metering
device. Frost may continue on the suction line back to the
compressor.
Often a partial restriction of any type can be found by feel,
as there is a temperature difference from one side of the
restriction to the other.
With a complete restriction, there will be no sound at the
metering device entrance. An amperage check of the
compressor with a partial restriction may show normal
current when compared to the unit specication. With a
complete restriction the current drawn may be considerably
less than normal, as the compressor is running in a deep
vacuum (no load.) Much of the area of the condenser will
be relatively cool since most or all of the liquid refrigerant
will be stored there.
The following conditions are based primarily on a system
in the cooling mode.
17