Page
8
Conclusion
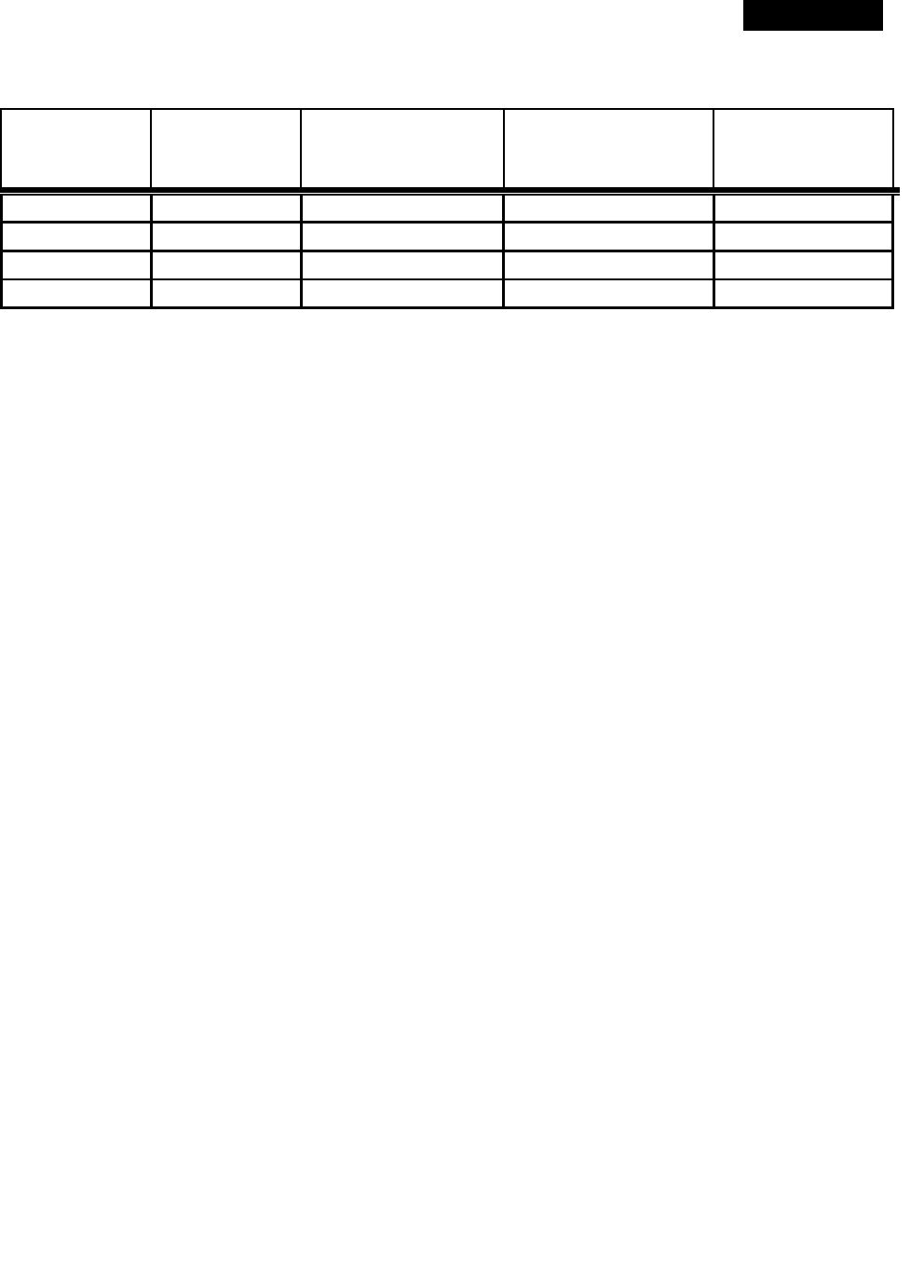
UV-Aire
Model
Airflow
velocity
(fpm)
Percent Reduction
of Bacteria
Percent Survival of
Bacteria
Log Reductions
of Bacteria
UV-18 500 93.31 6.69 1.17
UV-18 1000 71.99 29.01 0.54
UV-18X 500 99.00 0.95 2.02
UV-18X 1000 90.33 9.67 1.01
The testing showed the UV-Aire lamp yields at least a 90% reduction of the test bacteria
with a single airflow pass through a duct system at typical airflow rates. This efficiency
will not be the same for all bacteria and molds since each organism requires different
exposure times at the same UV output energy level.
At the higher velocity, the lamp still reduced the bacterial levels by at least 71 % at a 50%
decrease in the exposure time. Since the reduction efficiency is based on lamp UV
output and exposure time, the assumption can be made that decreasing the exposure
time to the UV light is similar to testing an organism that requires a higher UV energy
requirement to kill the bacteria. The log reductions in bacterial levels were very close to
theoretical values. Within the limits of testing accuracy, twice as many log reductions
(0.54 vs. 1.17 and 1.01 vs. 2.02) occurred with twice the exposure time.
This testing and the results clearly show that the exposure of the air to the UV light of the
UV-Aire will reduce levels of airborne bacteria.
Form #4291 08/01










