189
6.2. PREDICTING FAILURES USING THE TEST FUNCTIONS
The Test Functions can be used to predict failures by looking at how their values
change over time. Initially it may be useful to compare the state of these Test
Functions to the values recorded on the printed record of the final calibration
performed on your instrument at the factory, p/n 04307. Table 6-3 can be used as
a basis for ta
king action as these values change with time. The internal data
acquisition system (DAS) is a convenient way to record and track these changes.
Use APICOM to download and review this data from a remote location.
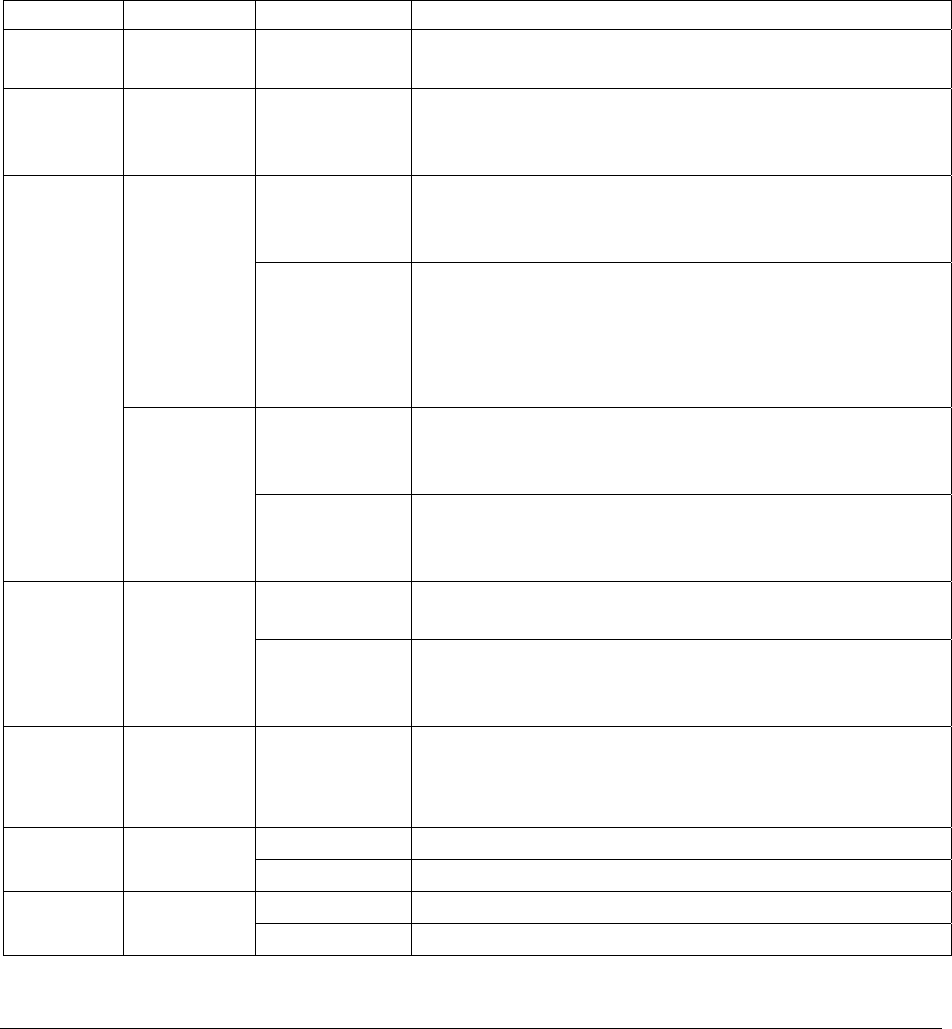
Table 6-3: Predictive Uses for Test Functions
FUNCTION CONDITION BEHAVIOR INTERPRETATION
STABILITY
Zero Cal Increasing
Pneumatic Leaks – instrument & sample system
Detector deteriorating
CO2 MEAS
Zero Cal Decreasing
Source Aging
Detector deteriorating
Optics getting dirty or contaminated
Increasing
Source Aging
Detector deteriorating
Contaminated zero gas (H2O)
Zero Cal
Decreasing
Source Aging
Detector deteriorating
GFC Wheel Leaking
Pneumatic Leaks
Contaminated zero gas (CO
2
)
Increasing
Source Aging
Pneumatic Leaks – instrument & sample system
Calibration system deteriorating
MR RATIO
Span Cal
Decreasing
Source Aging
GFC Wheel Leaking
Calibration system deteriorating
Increasing > 1”
Pneumatic Leak between sample inlet and Sample Cell
Change in sampling manifold
PRES
Sample
Decreasing > 1”
Dirty particulate filter
Pneumatic obstruction between sample inlet and Sample Cell
Obstruction in sampling manifold
PHT DRIVE
Any, but
with Bench
Temp at
48°C
Increasing
Mechanical Connection between IR-Detector and Sample Cell
deteriorating
IR-Photodetector deteriorating
Increasing
See MR Ratio - Zero Cal Decreasing above
OFFSET
Zero Cal
Decreasing
See MR Ratio - Zero Cal Increasing above
Increasing
See MR Ratio - Span Cal Decreasing above
SLOPE
Span Cal
Decreasing
See MR Ratio – Span Cal Increasing above
07272B DCN6552