Installer’s Information Manual Page 21
SECTION 13. MANIFOLD
PRESSURE ADJUSTMENT
You will need a 0 to 15 inch water manometer with 0.1 inch
resolution and a 1/8" NPT manual shut-off valve to measure
actual manifold pressure.
WARNING: Correct manifold pressure is
necessary for proper ignition and burner operation. Failure
to accurately adjust pressure could cause heat exchanger
failure.
Check gas-supply pressure first. Follow instructions in
Section 12, "Gas Supply Pressure and Pilot Adjustment."
1. Turn off gas at equipment shut-off valve in gas supply
line just ahead of furnace.
2. Remove three screws holding burner access panel in
place. Remove burner access panel.
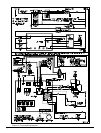
3. Remove plug from manifold pressure tap in gas
control. See Figure 13.
4. Install 1/8" NPT manual shut-off valve in hole vacated
by plug. Make sure shut-off valve is in off position.
5. Attach manometer to 1/8" NPT manual shut-off valve
just installed.
6. Slowly open equipment shut-off valve in gas supply line
just ahead of furnace. Start furnace following
"Operating Instructions" on front door.
7. Slowly open 1/8" NPT manual shut-off valve leading to
manometer.
8. Read manifold pressure on manometer.
9. Adjust manifold pressure by turning gas control
regulator adjusting screw clockwise to increase
pressure or turning counter-clockwise to decrease
pressure. Manifold pressure must be within allowable
range below:
?? Natural gas manifold pressure must be between
3.2 and 3.8 inches W.C.
?? Propane gas (LP) manifold pressure must be
between 9.7 and 10.3 inches W.C.
NOTE: For natural gas, if gas flow rate cannot be properly
set within these pressure ranges then you must change
main burner orifices to obtain proper gas flow rate.
10. Shut off furnace. Turn off gas at equipment shut-off
valve in gas supply line just ahead of furnace. Install
outlet-pressure-tap plug in gas control. Turn on gas.
11. Check regulator-adjustment-cover screw and gas
control plug for gas leaks. Use a commercial soap
solution made for leak detection.
12. Replace burner access panel using three screws
removed in step 2.
SECTION 14. CHECKING GAS
INPUT RATE
It is the installer's responsibility to see that the Btu input
rate of the furnace is properly adjusted. Under-firing could
cause inadequate heat, primary heat exchanger corrosion
and/or ignition problems. Over-firing could cause sooting,
flame impingement and/or overheating of heat exchanger.
WARNING: Failure to adjust furnace to the proper
firing rate could cause heat exchanger failure.
Depending on your local gas heating value and elevation,
you may need to adjust manifold pressure or change
orifices to get proper gas input rate. Check with your local
gas supplier to determine heating value (Btu/cu.ft.) of
natural gas in your area.
NOTE: If furnace is being installed at an altitude of more
than 2000 feet above sea level, you must derate the
furnace. See Section 15, "Derating For High Altitude."
NATURAL GAS INPUT RATE
Natural gas heating value (Btu/cu.ft.) can vary significantly.
Before starting natural gas input check, obtain gas heating
value at your location from local supplier. You will need a
stopwatch to measure actual gas input.
1. Gas supply pressure must be between 5 and 7 inches
W.C. for natural gas. See Section 12, "Gas Supply
Pressure and Pilot Adjustment."
2. Turn off all other gas appliances. You may leave pilots
on.
3. Start furnace following "Operating Instructions" on front
door. Let furnace warm up for 6 minutes.
4. Locate gas meter. Determine which dial has the
fewest cubic feet of gas and how many cubic feet per
revolution it represents. This is usually one-half, one or
two cubic feet per revolution.
5. With stopwatch, measure time it takes to consume two
cubic feet of gas.
?? If dial is one cubic foot per revolution, measure
time for two revolutions.
?? If dial is two cubic feet per revolution, measure
time for one revolution.
6. Divide this time by two. This gives average time for
one cubic foot of gas to flow through meter. Example:
If it took 58 seconds for two-cubic feet to flow, it would
take 29 seconds for one-cubic foot to flow.
7. Calculate gas input using this formula:
Gas Heating Value (Btu/cu.ft.)
X 3,600 sec/hr
Gas input = = Btu/hour
Time (Seconds for
one cubic foot of gas)