Troubleshooting
31
5.0 TROUBLESHOOTING
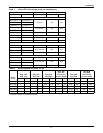
Table 23 Troubleshooting
Problem Cause Remedy
Unit will not start
No power to unit Check voltage at input terminal block.
Compressor contactor not pulling in
Check for 24VAC ±2VAC at control connections 1 & 2. If
no voltage, check control setting requires cooling. If there
is voltage, lockout relay may be energized. Check for
24VAC at control connections 2 & 3. If there is voltage,
see compressor high-discharge pressure/lockout relay.
Control voltage circuit breaker (at
transformer in evaporator module)
open
Locate short and reset circuit breaker.
Short cycle prevention control
Control software delays compressor 3 minutes from stop
to start.
Compressor high discharge
pressure/ lockout relay
Check for 24VAC ±2VAC at control connections 2 & 3.
Remove 24VAC signal at Connection 2 by turning indoor
unit control off, then back on, or by raising the setpoint to
remove the cab for cooling, then resetting to re-establish
operation.
High discharge
pressure
Insufficient air flow across
condenser coil
Check fan operation. Remove debris from coil and air
inlets.
High refrigerant charge Check refrigerant charge.
Low discharge pressure
Faulty head pressure control valve Replace if defective.
Compressor rotation in reverse
direction
Check for proper power phase wiring to unit and to
compressor motor.
Low suction pressure /
compressor cycling
Insufficient refrigerant in system Check for leaks; repair and add refrigerant.
Plugged filter drier Replace filter drier.
Improper superheat adjustment
Reset expansion valve for 10-15°F (5.6 to 8.4°C)
superheat at evaporator.
Defective liquid line solenoid valve Check valve and coil; replace if necessary.
Low compressor
capacity/ no cooling
Defective liquid line solenoid valve Check valve and coil; replace if necessary.
Plugged filter drier
Check pressure drop across filter drier. Replace filter
drier.
Low refrigerant charge
Check for normal system operating pressures. Refer to
abnormal pressure causes if applicable. Check for leaks.
Proper refrigerant charge is very important at low ambient
operation.
Compressor noisy
Loose compressor or piping
support
Tighten clamps.
Compressor rotation in reverse
direction
Check for proper power phase wiring to unit and to
compressor motor.
Pipe Rattle Loose pipe connections Check pipe connections.
Compressor running hot Compression ratio too high
Check for normal system operating pressures. Refer to
abnormal pressure causes if applicable.
Compressor motor
protectors tripping or
cycling
High discharge pressure Check for blocked condenser fan or coil.
High suction temperature
Check expansion valve and hot gas bypass valve setting.
Check liquid quenching valve operation.
Loose power or control circuit
wiring connection
Check all power and control circuit connections.
Defective motor
Check for motor ground or short. Replace compressor if
either condition is found.
Compressor cycles on
locked rotor
Low line voltage Check line voltage and determine location of voltage drop.
Compressor motor defective Check for motor winding short or ground.
Single phasing
Check voltage across all 3 legs at contactor. Correct
source of problem.
Motor burnout
Check control panel for welded
contactor contacts or welded
overload contacts.
Replace defective components.