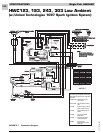
SPECIFICATIONS Magic-Pak: HW/HWC
2-34
SRM-HW/HWC 2/99
Detailed Sequence - HW
(w/Fenwal 05-29 Ignition Control)
Refer to Figure 2-6
POWER
Line Voltage
When the service disconnect switch is closed, power is
sent to the unit (unit in standby, no signal from the
thermostat). Power (208 - 230 volts A/C) is supplied
to both black wires located in the junction block on top
of the unit.
Line voltage will be present at the following locations:
First black wire
1. L-1 on the ignition module
2. Terminal on the transformer marked 208V or
240V (whichever is being used)
3. Circulating air blower capacitor terminal
Second black wire
1. Supplies power to the induced draft blower
2. Common terminal on the transformer
3. Terminal L-1 on the blower control board
Low Voltage (24 VAC)
With the unit at rest (no call from the thermostat), 24
volts A/C will be found at these points:
1. Red wire exiting the top of the unit
2. Terminal R on the blower control board
3. Terminal NO on the limit switch
4. Terminal on the transformer marked 24V
CALL FOR HEAT
Line Voltage
The thermostat closes the circuit between R and W.
The following is the sequence of operation for the line
voltage side of the unit:
1. Terminal TS (24-volt) energizes on the ignition
control, causing a relay in the ignition control to
close. This sends line voltage to the terminal
marked IND, causing the induced draft blower to
start.
2. When W is energized, a 24-volt signal is also sent
to the W terminal on the blower control board.
The 24-volt signal starts the timer on the blower
control board. After 60 seconds, the relay on the
blower control board closes. This sends line
voltage from the terminal marked L-1 to the terminal
marked H on the blower control board, starting
the circulating air blower. The induced draft
blower and the circulating air blower continue to
operate until the heat call is satisfied, interrupting
the circuit between R and W. The ignition control
de-energizes the induced draft blower relay,
interrupting L-1 power to the induced draft blower.
The induced draft blower stops several seconds
later. The W terminal on the blower control board
de-energizes, starting a 90-second blower “off”
delay. This interrupts the line voltage to the circu-
lating air blower and after 90 seconds, the blower
shuts down.
Low Voltage
1. A call for heat closes the circuit in the thermostat
between R and W, sending a 24-volt signal to the
white wire on the unit.
2. The white wire goes to the C terminal on the limit
switch, ignition control terminal TS and terminal
W on the blower control board.
3. When W energizes, the timer starts a countdown to
circulating air blower “on”. The blower starts in
approximately 60 seconds.
4. The 24-volt signal sent to the TS terminal closes a
relay in the ignition control. This starts the
induced draft blower by energizing terminal IND
on the ignition control.
5. As the induced draft blower comes up to speed
and creates enough negative pressure, the pres-
sure switch closes. The 24-volt signal is sent from
the pressure switch to one side of the Normally
Closed manual reset rollout switch. If the
rollout switch is closed, the 24-volt signal is
passed through the switch to the P.SW terminal on
the ignition control. This initiates a 30-second
pre-purge period.
6. After the 30-second pre-purge period, a trial for
ignition starts by energizing the spark terminal and
the V1 terminal simultaneously. The 24-volt signal
from V1 energizes the gas valve solenoid, causing
it to open. These actions cause the burners to light.
7. After the burners are lit, a flame sense is picked up
by the flame sense rod located at the opposite
end of the burner rack from the spark electrodes.
The flame sense signal is sent to the S1 terminal of
the ignition control. The unit continues to operate
as long as W is energized.